How does a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) process image data?

- CNNs process images by applying convolution filters that scan the image
to detect small patterns such as edges and textures. These filters generate
feature maps that highlight important regions of the image. - Pooling layers then downsample these feature maps to reduce dimensionality
while retaining key information. Deeper layers detect increasingly complex
patterns such as shapes and objects. - Finally, fully connected layers convert the extracted features into
predictions such as image classifications.
Explain how gradient descent updates model parameters during training.
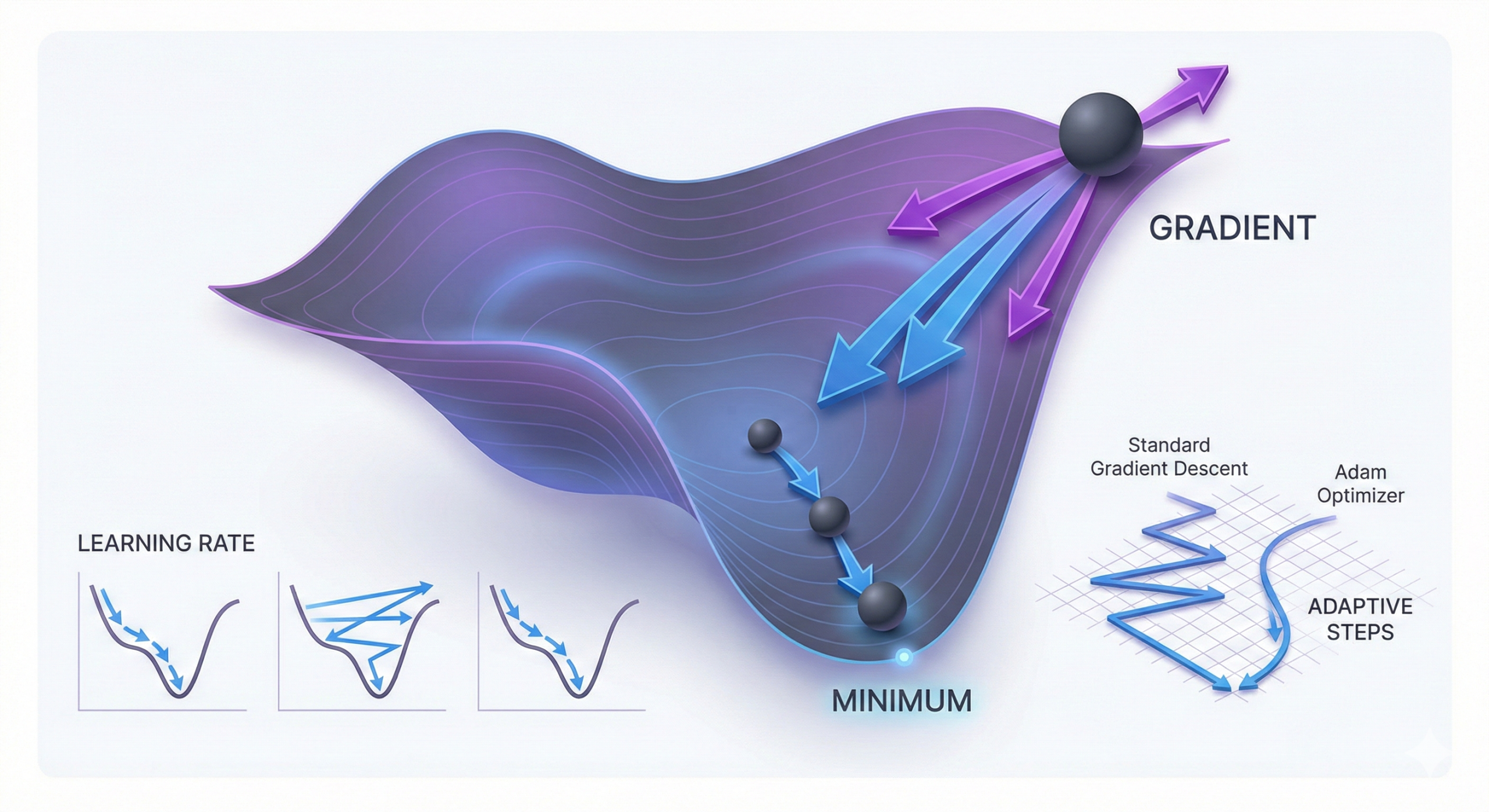
Gradient descent is an optimization algorithm that computes
the slope (gradient) of the loss function with respect to model parameters,
indicating the direction in which the error decreases.
The algorithm updates model weights by moving in the direction
opposite to the gradient. A carefully chosen
learning rate ensures stable convergence without overshooting
the optimal point.
This process repeats iteratively until the model reaches a local or global
minimum. Advanced optimizers such as Adam improve training
speed and stability by automatically adjusting step sizes.
What is overfitting, and why is it harmful in AI models?
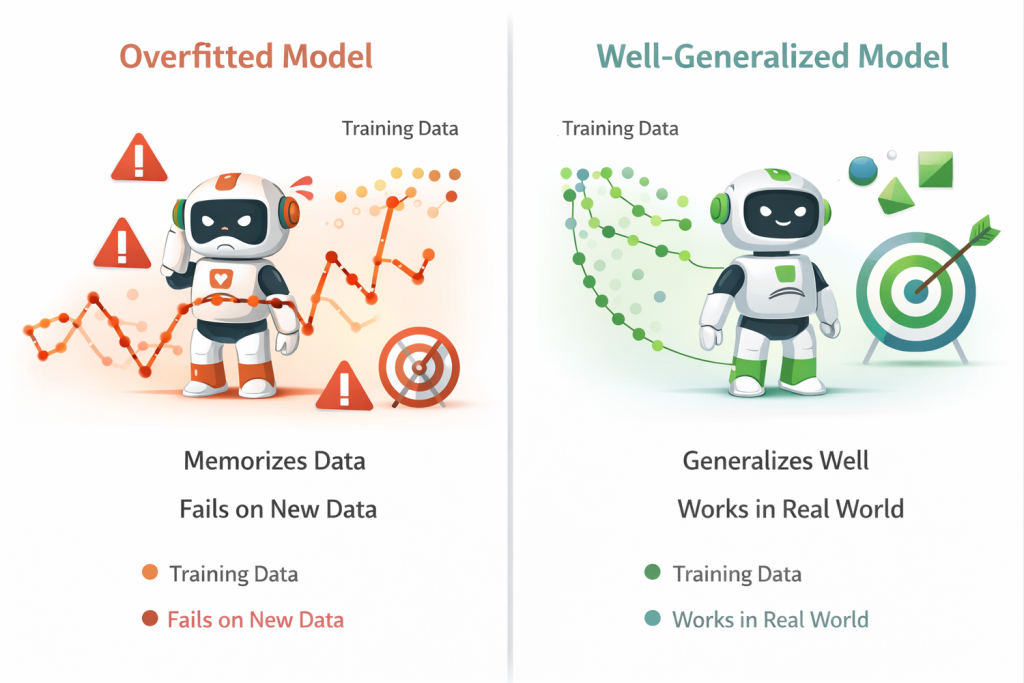
Overfitting occurs when a model learns noise and irrelevant
patterns present in the training data, which reduces its ability to
generalize to unseen data.
Key characteristics of overfitting include:
- Excellent performance on training data
- Poor accuracy on real-world or unseen data
- Learning noise instead of meaningful patterns
- High sensitivity to small input changes
- Unstable and unreliable predictions
Common solutions to prevent overfitting:
- Apply dropout techniques
- Use regularization methods (L1/L2)
- Collect more diverse and representative data
- Use k-fold cross-validation for proper evaluation
How does a transformer model handle sequential data differently from RNNs?
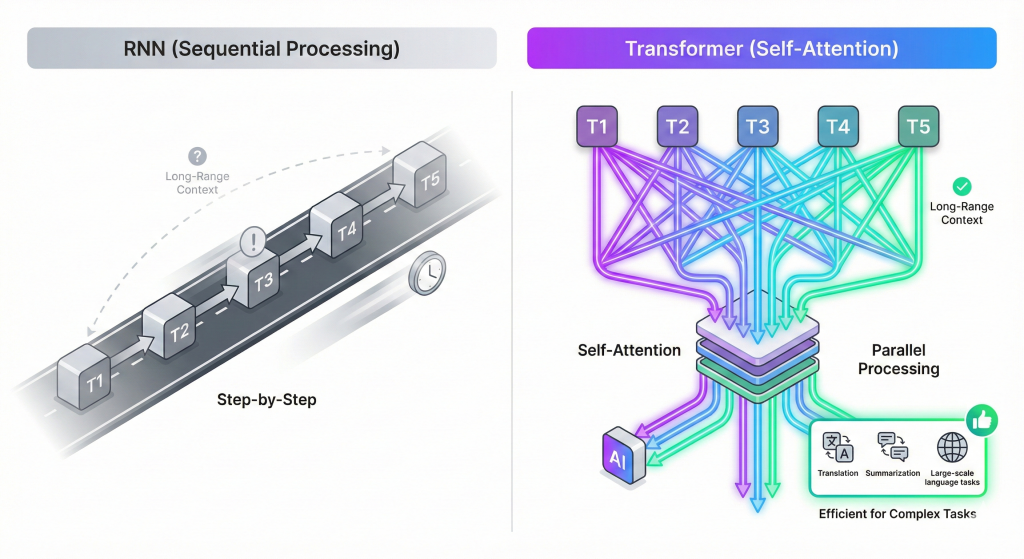
Transformers use self-attention mechanisms to analyze
entire input sequences at once, instead of processing data step-by-step
like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs).
Key advantages of transformers include:
- Capture long-range dependencies without vanishing gradient problems
- Process data in parallel, significantly speeding up training
- Use self-attention to identify relationships between all tokens
- Improve contextual understanding of sequences
As a result, transformers outperform RNNs in tasks such as
machine translation, text summarization,
and other large-scale natural language processing (NLP) applications.
What are the key differences between traditional machine learning and deep learning?
| Feature | Traditional ML | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Engineering | Manual | Automatic (learned) |
| Data Requirement | Low / Moderate | Very High |
| Compute | CPU sufficient | Requires GPU / TPU |
| Best For | Structured data | Images, text, audio |
Traditional machine learning models rely heavily on handcrafted features
and perform well on small, structured datasets.
Deep learning eliminates much of this manual effort by automatically
extracting features using multiple neural network layers.
While traditional ML models train faster, deep learning typically achieves
higher accuracy on complex tasks. Both approaches complement each other,
and the choice depends on the problem domain, data size, and available resources.
Compare supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
| Learning Type | Input | Output | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised | Labeled data | Predictions | Classification, regression |
| Unsupervised | Unlabeled data | Patterns / groups | Clustering, anomaly detection |
| Reinforcement | Reward-based feedback | Optimal actions | Robotics, gaming, automation |
Supervised learning uses labeled datasets to train models to predict outcomes,
while unsupervised learning detects hidden structure in data without labels.
Reinforcement learning teaches agents to make decisions by maximizing rewards
through interaction with an environment. Each technique addresses different
types of problems, and selection depends on data availability and business goals.
Compare CNNs and RNNs in terms of architecture and use cases.
| Feature | CNN | RNN |
|---|---|---|
| Input Type | Images, grids | Sequences (text / time series) |
| Core Operation | Convolution | Recurrence |
| Strength | Spatial feature extraction | Temporal dependency modeling |
| Weakness | Poor with sequences | Slow training, vanishing gradients |
- CNNs perform well in visual tasks by detecting spatial patterns across pixels,
while RNNs focus on capturing temporal dependencies in sequences such as
sentences or time-based data. CNNs support parallel computation, whereas
RNNs process data sequentially. - Transformers have largely replaced RNNs in many applications due to improved
speed and accuracy. However, each architecture remains useful depending on
the type and structure of the input data.
What is the role of activation functions in neural networks?
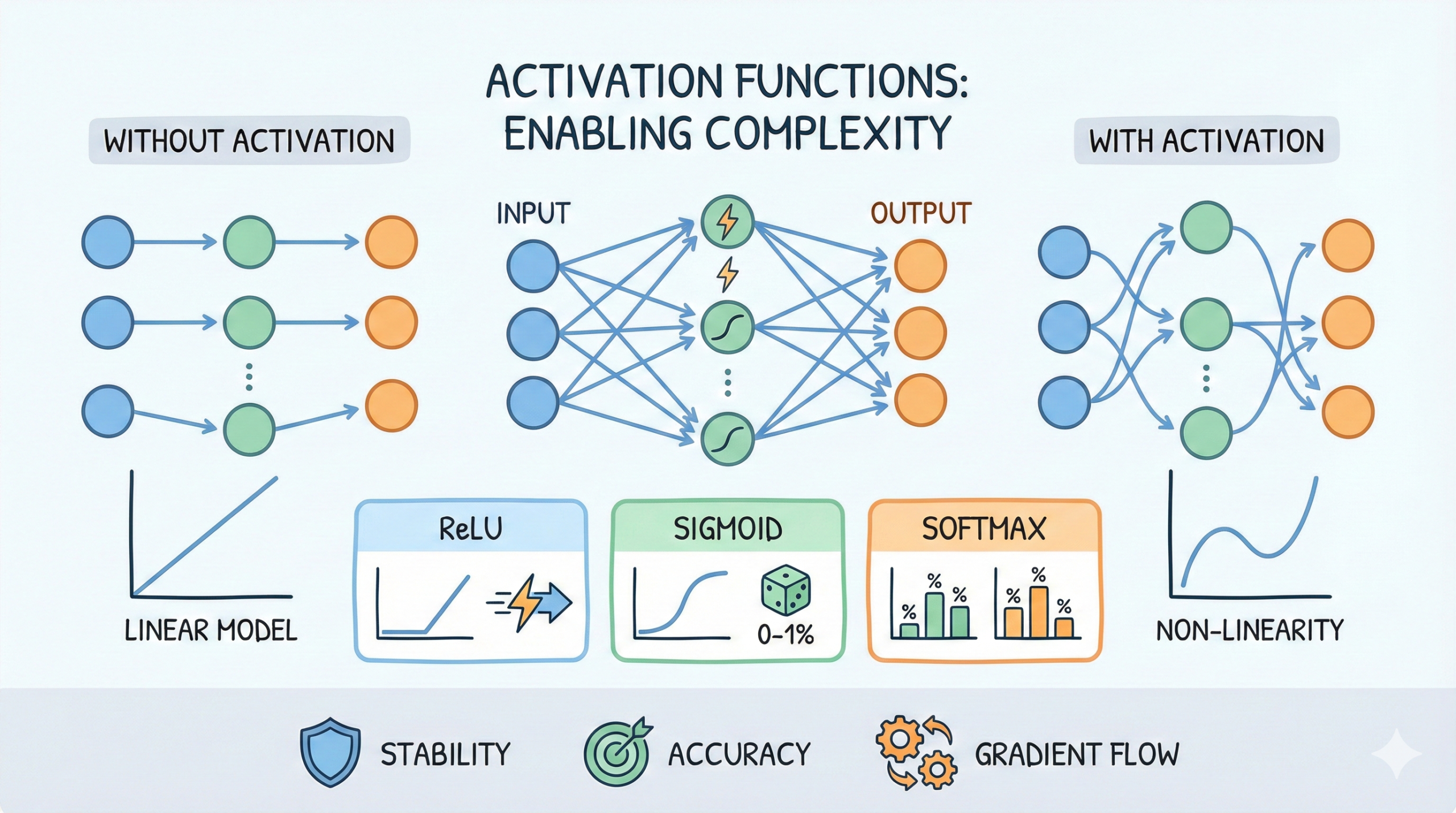
Activation functions introduce non-linearity into a neural
network, allowing it to learn complex patterns and relationships in data.
Without activation functions, even deep networks would behave like simple
linear models.
Functions such as ReLU improve convergence speed by reducing
saturation and enabling efficient gradient flow during training.
Sigmoid and softmax activation functions are
essential when modeling probabilities in classification tasks. Choosing the
right activation function directly impacts model stability, accuracy, and
gradient behavior.
How does backpropagation update weights inside deep neural networks?
Backpropagation is the learning process used in neural networks
to adjust model weights by calculating how much each parameter contributes
to the final prediction error.
Key steps involved in backpropagation:
- Gradients are computed using the chain rule across network layers
- Each gradient indicates how a weight influences the overall loss
- The optimizer updates weights in the direction that reduces error
- This process is repeated for every training batch
- Training continues until the model reaches stable convergence
Proper weight initialization and techniques such as normalization help maintain
stable gradient flow, prevent training instability, and improve overall model
performance.
Explain the importance of feature engineering in AI pipelines.
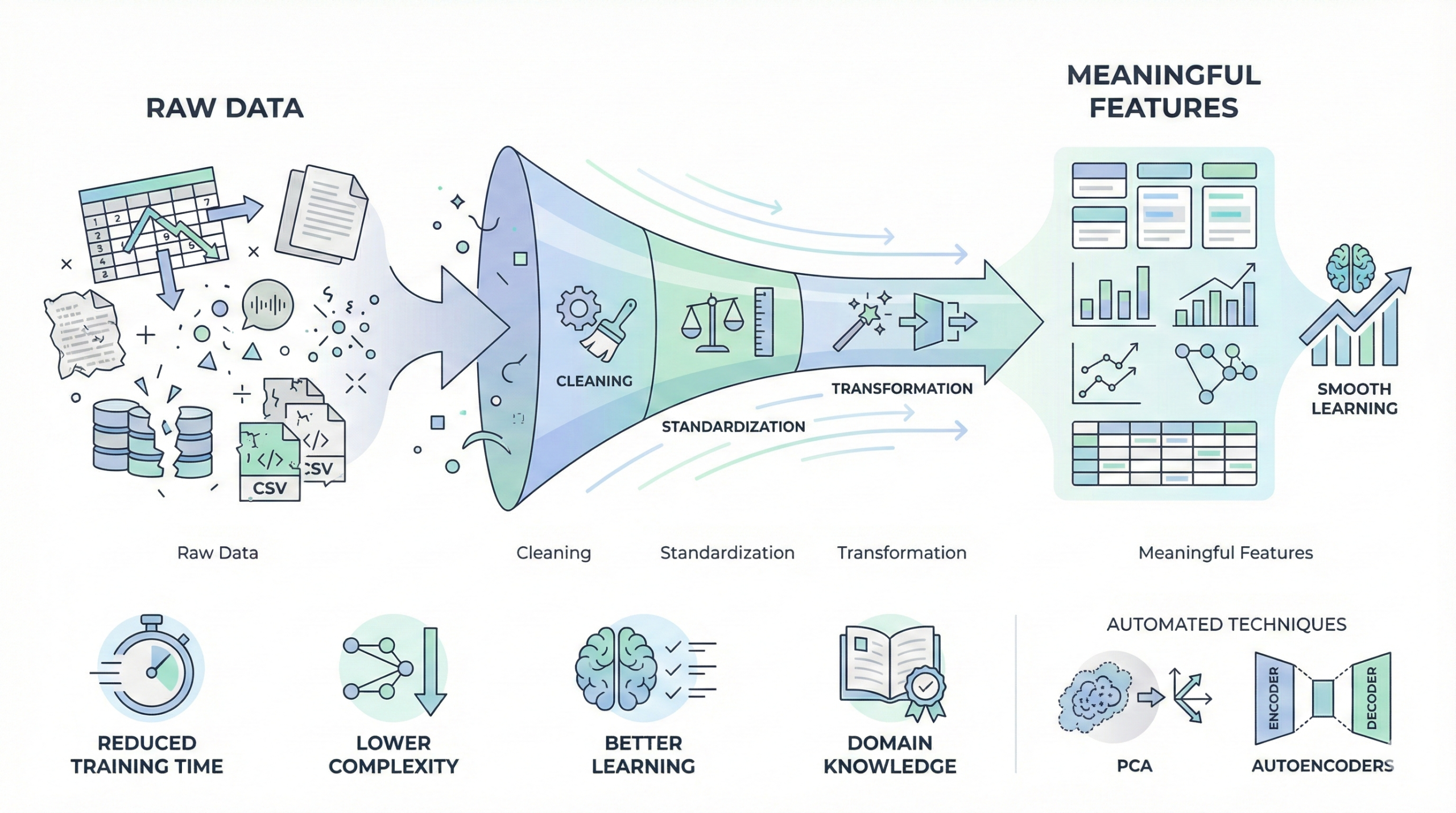
Feature engineering transforms raw data into meaningful
representations that improve model learning and performance.
High-quality features reduce model complexity and training time.
Even deep learning models benefit from cleaned and standardized input.
Domain knowledge plays a key role in selecting impactful variables,
while automated techniques such as PCA and
autoencoders complement manual feature creation.
What is the purpose of regularization in model training?
Regularization is a technique used in machine learning to
reduce overfitting by discouraging models from becoming too complex.
It helps models perform better on unseen, real-world data.
Common regularization methods include:
- L1 regularization encourages sparsity by driving less
important feature weights toward zero - L2 regularization controls large weight values and keeps
the model smoother and more stable - Dropout randomly disables neurons during training,
forcing the network to learn more robust patterns
When tuned correctly, regularization strikes a balance between
model flexibility and stability, improving generalization
without hurting learning capacity.
How does batch normalization improve neural network training?
Batch normalization is a technique that normalizes activations
between neural network layers, helping stabilize and speed up the learning
process. By reducing internal covariate shift, it allows models to train
more efficiently and converge faster.
Key benefits of batch normalization:
- Stabilizes training by keeping activations within a consistent range
- Enables faster convergence during optimization
- Allows the use of higher learning rates without instability
- Provides a mild regularization effect that improves generalization
- Supports deeper network architectures
Real-life example:
Think of batch normalization like adjusting the volume levels of different
speakers before a live concert. If one speaker is too loud or too quiet,
the overall sound becomes distorted. Batch normalization keeps all signals
balanced, so the network learns smoothly without sudden disruptions.
What is the role of autoencoders in data science?
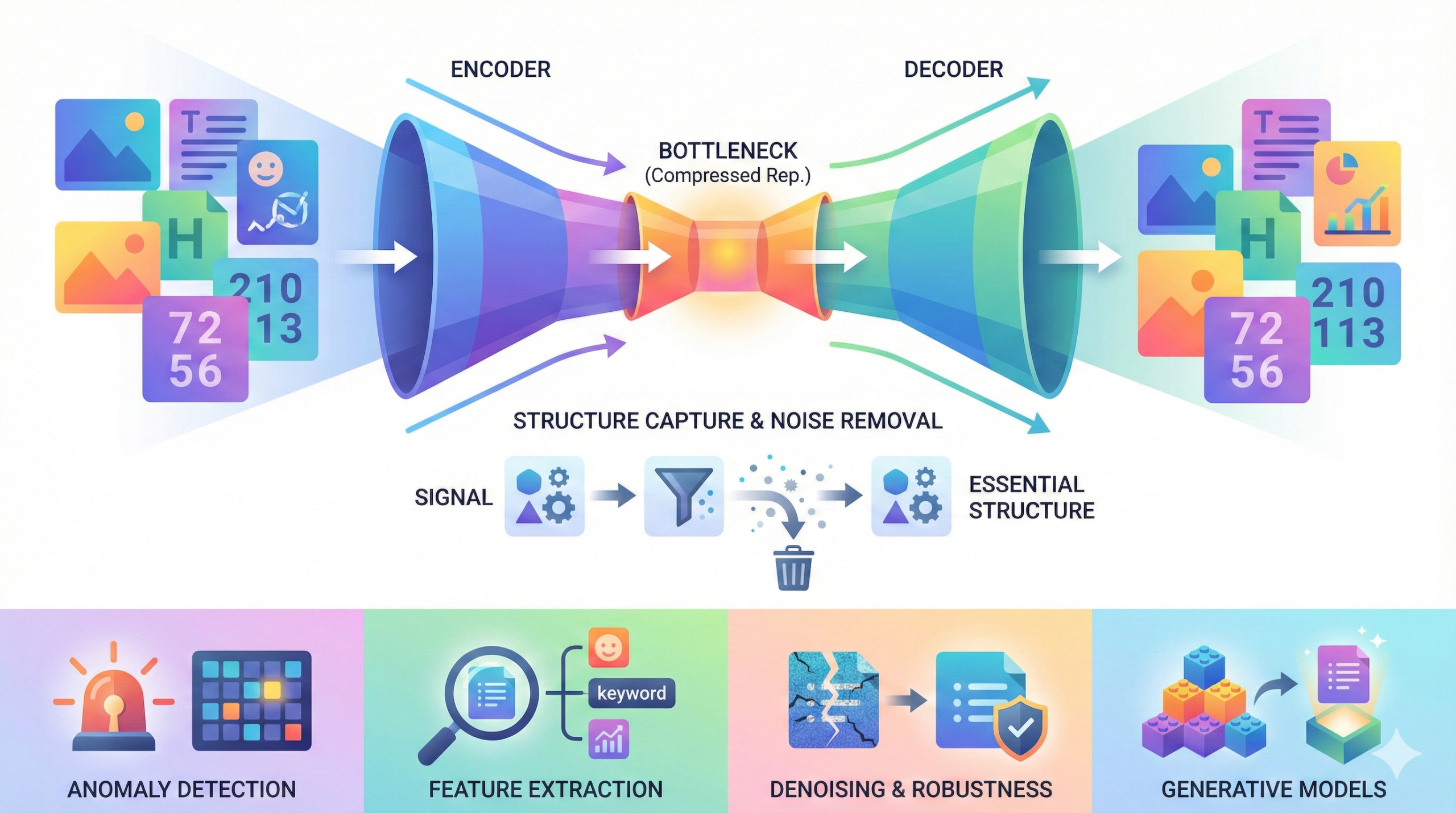
Autoencoders learn compressed representations of data by
passing inputs through an encoder and then reconstructing them using a decoder.
This process captures the essential structure of the data while reducing noise.
Autoencoders are commonly used for tasks such as anomaly detection
and feature extraction.
Variants like denoising autoencoders are designed to handle
corrupted or incomplete inputs more robustly.
Autoencoders also act as foundational components in many
generative models.
Why is data preprocessing critical before model training?
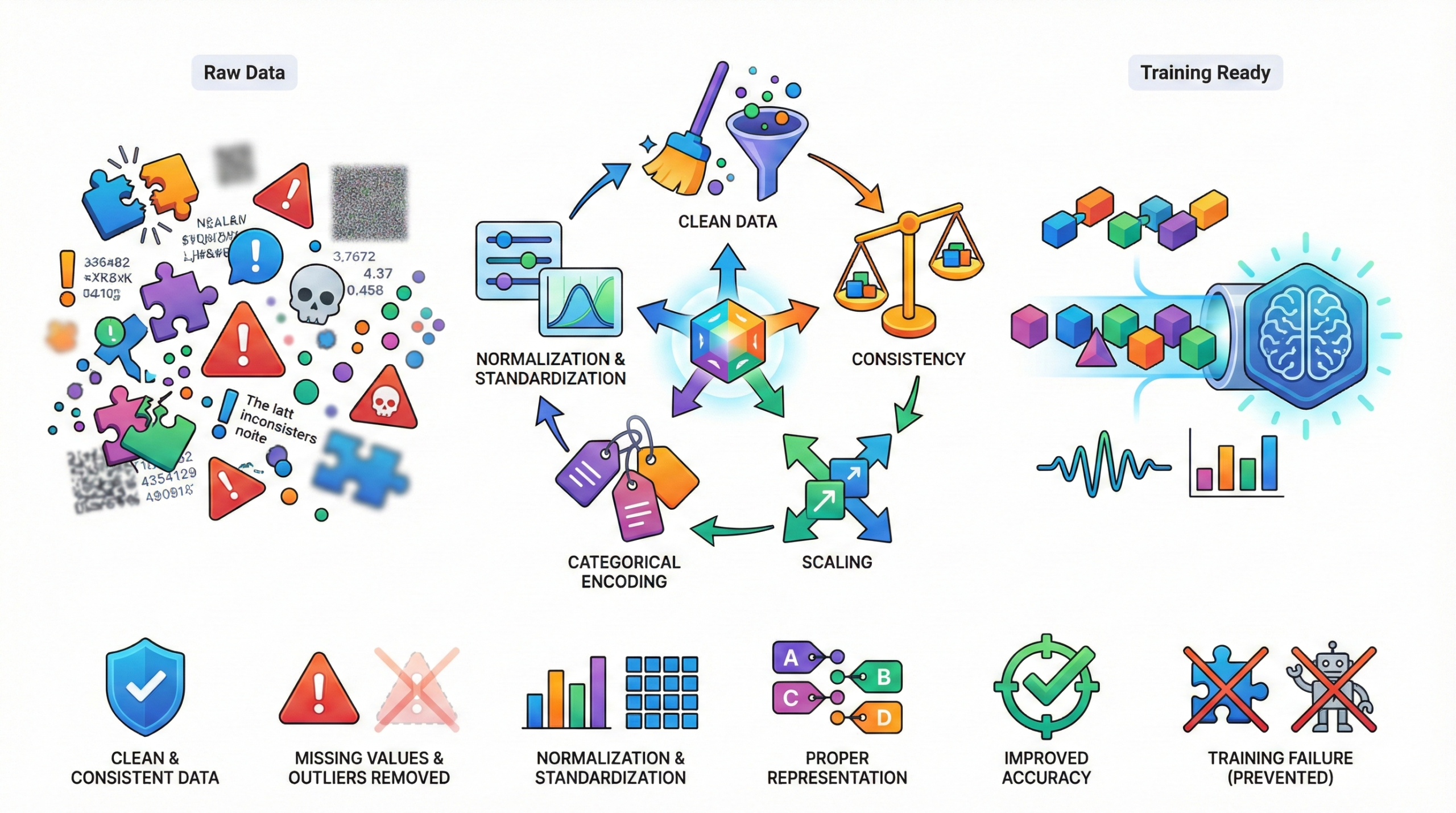
Preprocessing ensures that data is clean, consistent, and
scaled appropriately before training a machine learning model.
Issues such as missing values, outliers, and inconsistent formats
can significantly degrade model performance.
Techniques like normalization and
standardization improve numerical stability during
optimization, while encoding categorical variables ensures proper
representation for learning algorithms.
High-quality preprocessing improves accuracy and reduces training failures.
Explain reinforcement learning in data-driven decision-making.
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a machine learning approach
where an agent learns how to act optimally in a dynamic environment by
interacting with it and observing the outcomes of its actions.
Key characteristics of reinforcement learning:
- Agents learn through trial and error rather than labeled data
- Actions are guided by rewards and penalties
- Decisions are sequential, where past actions affect future outcomes
- The goal is to maximize long-term cumulative reward
Common applications and algorithms:
- Algorithms such as Q-learning and policy gradients
- Used in robotics, automation, and control systems
- Applied in recommendation engines, gaming, and navigation
Reinforcement learning is especially effective in real-world scenarios
where decisions must adapt continuously to changing conditions.
How do LSTM networks overcome RNN limitations?
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are a special type of
recurrent neural network designed to handle long-term dependencies
in sequential data more effectively than traditional RNNs.
Key features of LSTMs:
- Use gating mechanisms to control how information flows over time
- Address the vanishing gradient problem found in standard RNNs
- Maintain memory cells that store information across long sequences
- Retain relevant context while discarding unnecessary data
Practical use cases:
- Speech recognition systems
- Language translation models
- Time-series forecasting and sequence prediction
Although transformer-based models are now widely used, LSTMs remain
valuable in compact deployments where memory efficiency and simpler
architectures are preferred.
What is the purpose of dimensionality reduction in AI?
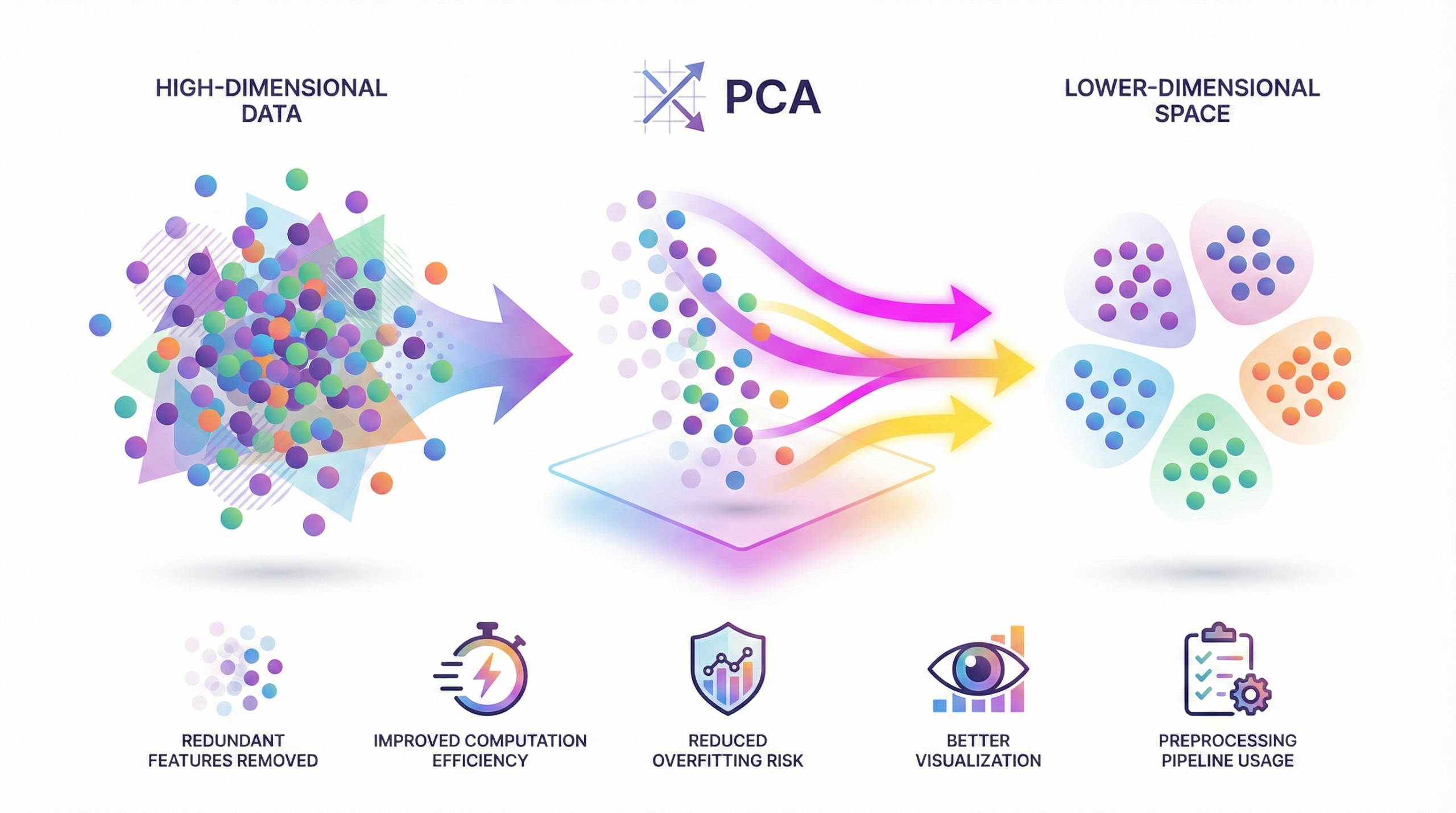
Dimensionality reduction is a data preprocessing technique
used to remove redundant or irrelevant features while preserving the most
important information in a dataset.
Why dimensionality reduction is important:
- Reduces noise by eliminating unnecessary features
- Improves computational efficiency and training speed
- Lowers the risk of overfitting in machine learning models
- Makes high-dimensional data easier to visualize and understand
- Is commonly applied during data preprocessing pipelines
Common techniques used:
- PCA (Principal Component Analysis) projects data into a
lower-dimensional space while retaining maximum variance
Real-life example:
In image recognition, a single image may contain thousands of pixel values.
Dimensionality reduction helps compress this information into fewer meaningful
features, allowing models to recognize faces or objects faster without
processing every individual pixel.
How does Explainable AI (XAI) improve data science workflows?
Explainable AI (XAI) focuses on making machine learning
model decisions understandable to humans. Instead of acting like a
black box, XAI reveals why a model produced a particular output.
Key benefits of Explainable AI:
- Improves transparency by explaining how predictions are made
- Identifies influential features using tools like SHAP and LIME
- Helps detect bias and ensures fairness in sensitive applications
- Builds trust among users, regulators, and stakeholders
- Assists data scientists in debugging and refining models
Real-life example:
In healthcare, if an AI system predicts a high risk of heart disease,
doctors need to know whether the decision was based on age, blood pressure,
cholesterol levels, or lifestyle factors. XAI tools clearly highlight
these contributing factors, allowing medical professionals to trust
and validate the model’s recommendation.
What are embeddings, and why are they important in AI?
Embeddings are a way of representing categorical or text data
as dense numerical vectors, allowing machine learning models to understand
relationships between items more effectively.
Key points about embeddings:
- Convert words or categories into compact numerical vectors
- Capture semantic relationships that one-hot encoding cannot
- Place similar words or items closer together in vector space
- Reduce dimensionality while preserving meaning
Practical usage and impact:
- Word embeddings such as Word2Vec and GloVe
enable contextual understanding in language models - Improve performance in natural language processing tasks
- Enhance recommendation systems by learning user–item relationships
- Serve as core building blocks in modern models, including transformers
By learning meaningful representations from data, embeddings help models
generalize better and make more accurate predictions in real-world applications.










