Q1. What is BeautifulSoup and why is it used in Python?
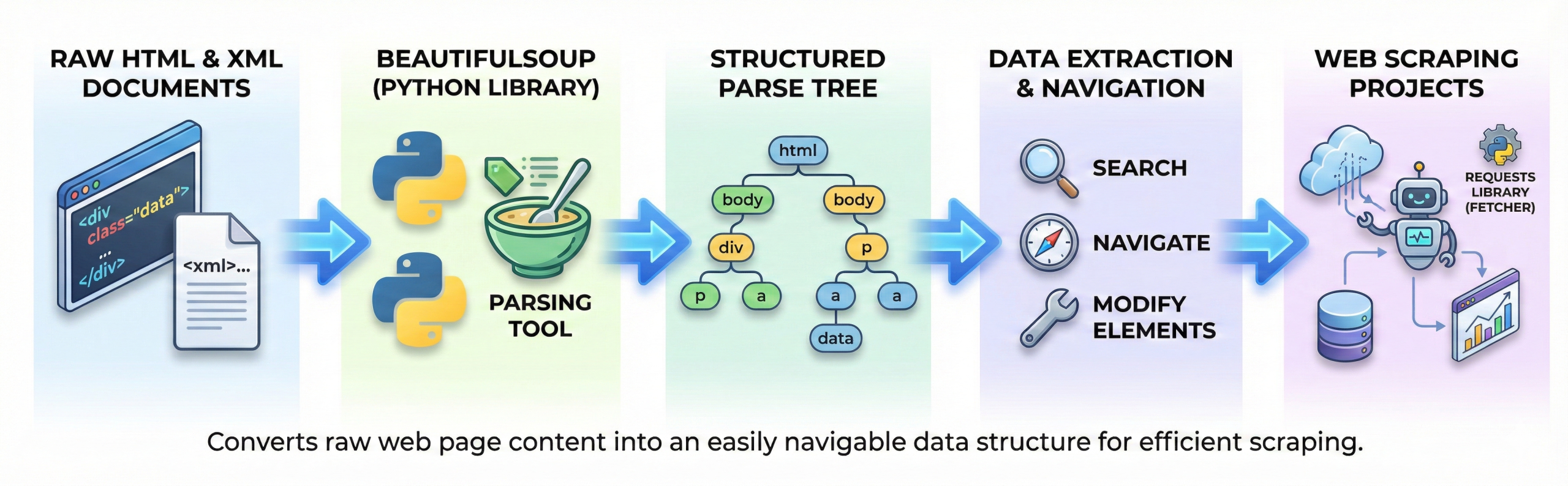
BeautifulSoup is a Python library used for parsing HTML and XML documents.
It helps extract data from web pages by converting raw HTML into a structured parse tree.
This makes it easy to navigate, search, and modify elements. BeautifulSoup is commonly used in web scraping projects. It works well with libraries like requests for fetching web content.
Q2. How does BeautifulSoup parse an HTML document?
BeautifulSoup converts raw HTML into a structured format that Python can understand and work with easily.
When you load HTML into BeautifulSoup, it organizes the content into a tree-like structure, similar to the DOM (Document Object Model) used in browsers. In this structure:
- Each HTML tag becomes a node
- Tags can have parent, child, and sibling relationships
- You can navigate through the structure easily
This makes messy or unstructured HTML much easier to search, filter, and extract data from.
Instead of reading HTML as plain text, you can interact with it like a structured object.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_content = """
<html>
<body>
<h1>Main Title</h1>
<p class="info">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="info">Another paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, "html.parser")
# Accessing elements
title = soup.h1
first_paragraph = soup.find("p")
all_paragraphs = soup.find_all("p")
print("Title:", title.text)
print("First Paragraph:", first_paragraph.text)
print("All Paragraphs:")
for p in all_paragraphs:
print("-", p.text)
Q3. How does BeautifulSoup extract elements from a web page?
BeautifulSoup extracts elements using methods like find() and find_all(). These methods search HTML tags based on tag name, class, id, or attributes.
Once found, text and attributes can be accessed easily.
This enables structured scraping of headings, links, tables, and content. It simplifies data extraction from complex pages.
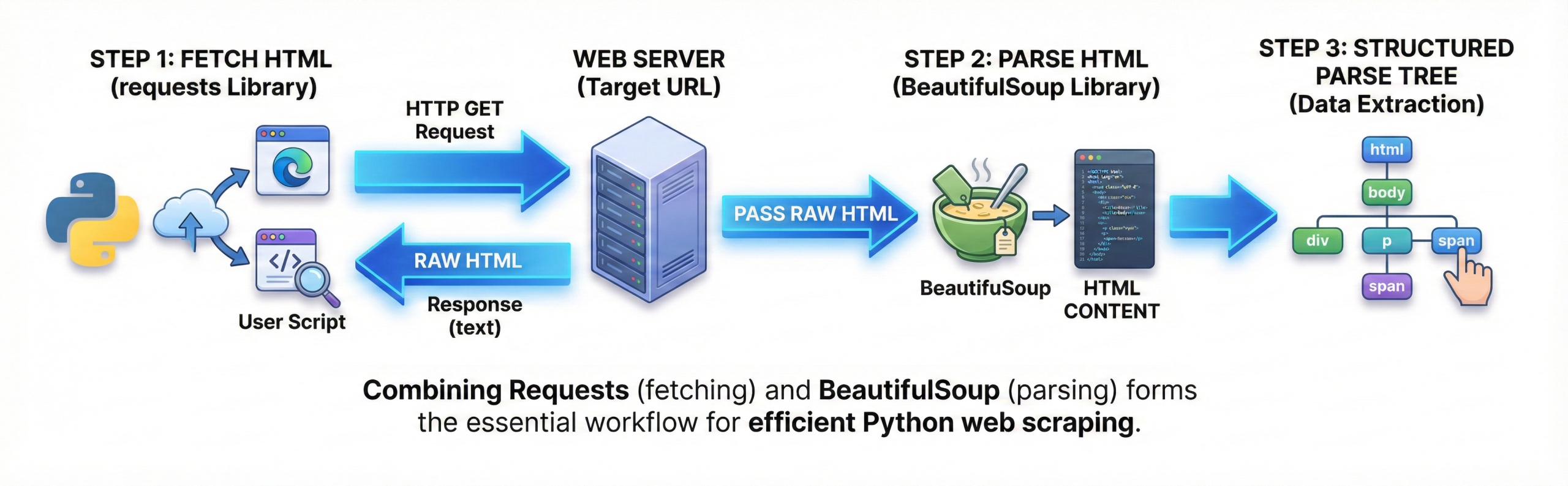
Q4. How does BeautifulSoup work with the requests library?
Requests fetches the HTML content from a URL, while BeautifulSoup parses it.
The response text from requests is passed into BeautifulSoup. This combination is the most common scraping workflow.
Requests handles HTTP communication; BeautifulSoup handles parsing. Together they form the backbone of Python web scraping.
Q5. Difference between BeautifulSoup and Selenium
| Feature | BeautifulSoup | Selenium |
| Type | HTML parser | Browser automation |
| JavaScript | Not supported | Supported |
| Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Use Case | Static pages | Dynamic pages |
Q6. Difference between find() and find_all().
| Method | Returns | Use Case |
| find() | First match | Single element |
| find_all() | List of matches | Multiple elements |
| Output | Tag | List of tags |
| Usage | Quick lookup | Full extraction |
Q7. Difference between .text and .get_text().
| Attribute | Purpose | Output |
| .text | Direct text | Raw text |
| .get_text() | Clean text | Stripped text |
| Whitespace | May include | Cleaner |
| Use Case | Simple | Preferred |
Q8. Difference between HTML parser and lxml parser
| Parser | Speed | Accuracy |
| html.parser | Medium | Good |
| lxml | Fast | Very high |
| Installation | Built-in | External |
| Use Case | Simple scraping | Large pages |
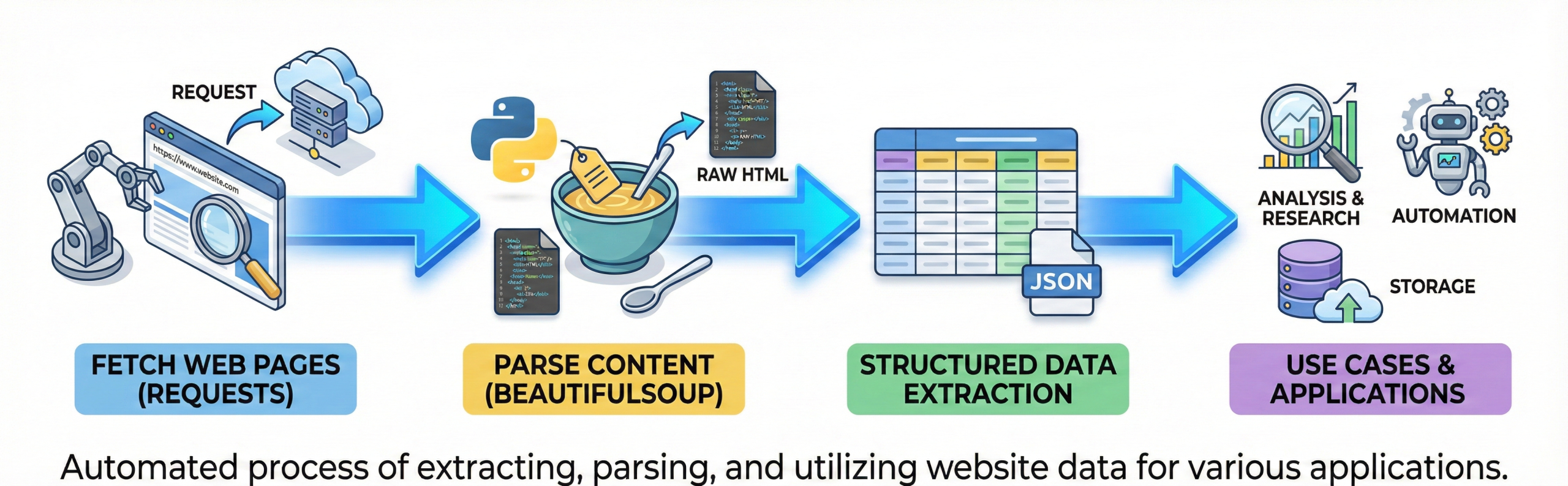
Q9. What is web scraping?
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites automatically. It involves fetching web pages and parsing their content.
Python libraries like BeautifulSoup make scraping easy. Scraped data is used for analysis, research, and automation. Interviews often test this basic concept.
Q10. How do you install BeautifulSoup?
It works with Python 3.The library requires a parser such as html.parser or lxml.
Installation is simple and quick. This is a common beginner question.
Q11. What is a parser in BeautifulSoup?
A parser is a tool that reads HTML or XML content and converts it into a structured format that Python can understand.
When you pass raw HTML to BeautifulSoup, the parser processes that text and builds a tree-like structure (similar to the DOM in web browsers). This structure allows you to easily search, navigate, and extract data from the document.
In simple words, the parser transforms messy HTML code into an organized hierarchy of tags and elements.
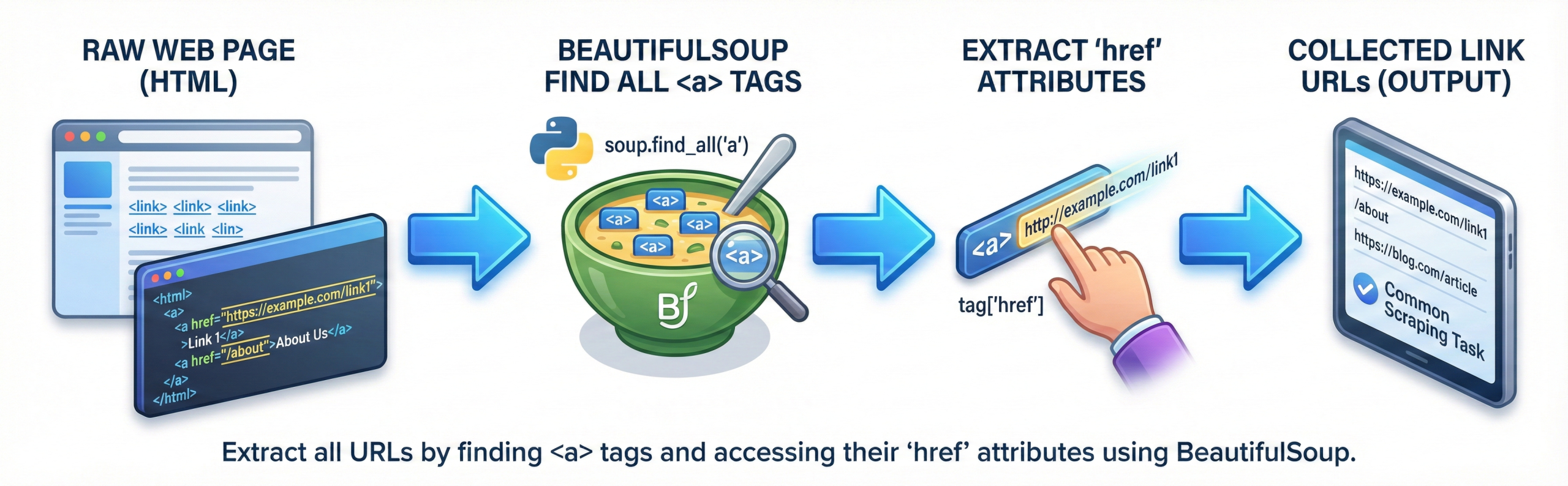
Q12. How do you get all links from a web page?
Links are extracted by finding all <a> tags. The href attribute contains the URL.
BeautifulSoup accesses attributes using dictionary syntax. This is a very common scraping task. Interviewers often ask this.
Q13. How do you extract attributes from HTML tags?
In BeautifulSoup, you can get attributes like href, class, or id using tag[‘attribute’] or tag.get(‘attribute’).
The bracket method works fine, but it throws an error if the attribute is missing.
Using get() is safer because it returns None instead of stopping the program.
This is commonly used when scraping links, images, or structured data from web pages.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = '<a href="https://example.com" class="link">Visit</a>'
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
tag = soup.find("a")
print(tag['href']) # Using bracket method
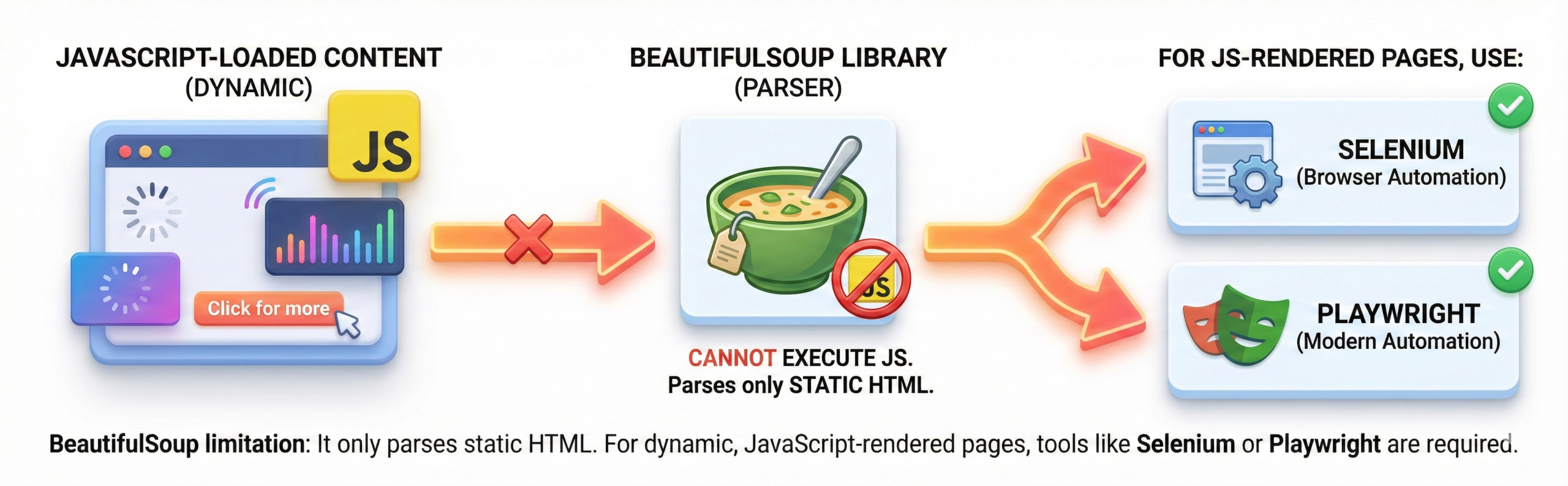
print(tag.get('class')) # Using get() methodQ14. Can BeautifulSoup handle JavaScript-loaded content?
No, BeautifulSoup cannot execute JavaScript. It only parses static HTML received from the server. For JavaScript-rendered pages, tools like Selenium or Playwright are used.
This limitation is frequently asked in interviews. Understanding this avoids scraping mistakes.
Q15. How do you handle missing tags in BeautifulSoup?
While scraping a website, you won’t always get the exact tags you expect. Some pages may not contain certain elements, and if you try to access them directly, your script can break with an error.A simple and practical way to avoid this is to check if the tag exists before using it. Just store the result of find() in a variable and use an if condition to confirm it’s not None.
When working with attributes, it’s better to use the get() method instead of square brackets. If the attribute doesn’t exist, get() safely returns None instead of crashing your program.
Handling missing tags properly keeps your scraper stable and prevents unnecessary runtime errors, especially when working with large or unpredictable websites.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = "<html><body><h1>Title</h1></body></html>"
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
# Try to find a paragraph tag (which does not exist)
para = soup.find("p")
if para:
print(para.text)
else:
print("Paragraph tag not found")
# Safe attribute access
link = soup.find("a")
if link:
print(link.get("href"))
Q16. What is prettify() used for?
prettify() formats HTML in a readable way. It adds indentation and line breaks.
It is useful for debugging and understanding page structure. It does not change data extraction. This method helps beginners visualize HTML.
Q17. How do you scrape table data using BeautifulSoup?
Tables are scraped by locating <table>, <tr>, <th>, and <td> tags. Rows and columns are extracted in loops.
Data is often stored in lists or DataFrames. This is a very common interview use case. Tables are widely scraped.
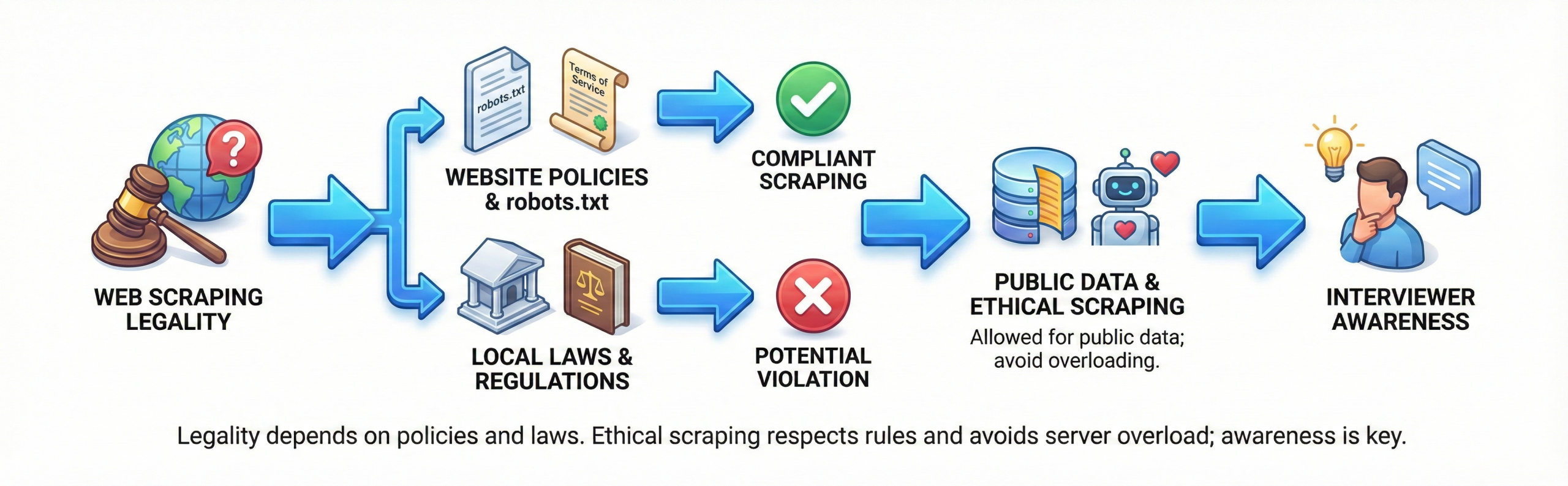
Q18. Is web scraping legal?
Web scraping legality depends on website policies and local laws. Many sites specify rules in robots.txt.
Scraping public data is often allowed. Ethical scraping avoids overloading servers. Interviewers expect awareness of this.
Q19. What is robots.txt?
robots.txt tells bots which pages can be accessed.
It helps protect sensitive routes. Scrapers should respect robots.txt rules.
Ignoring it may lead to IP bans. This is an important ethical consideration.
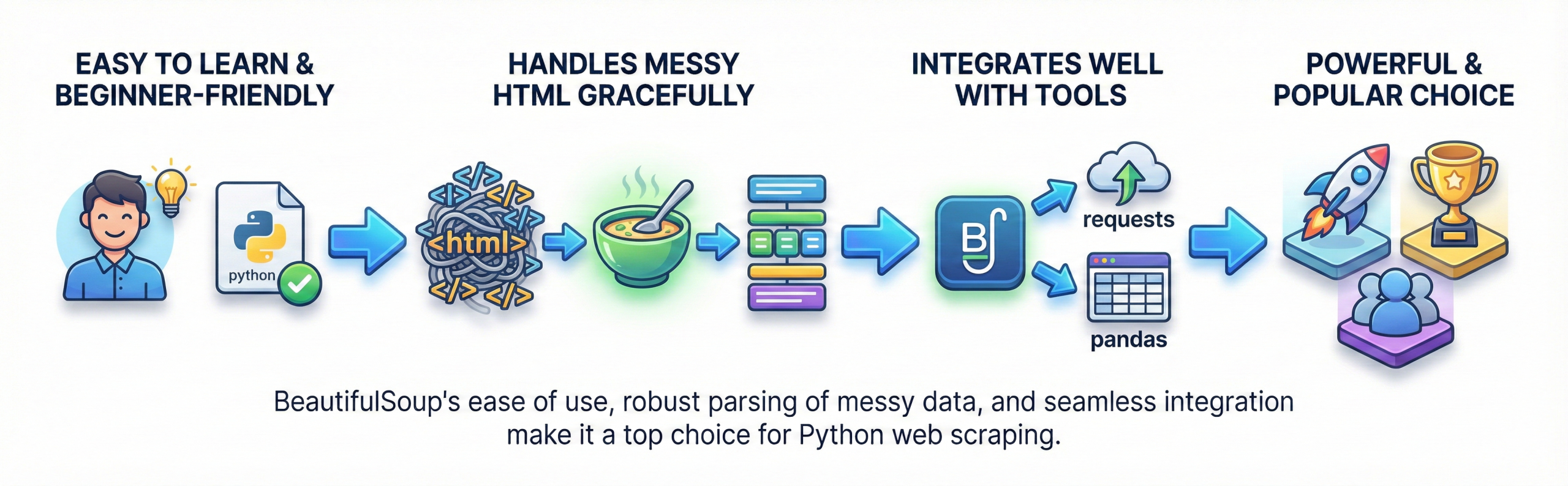
Q20. Why is BeautifulSoup popular among Python developers?
BeautifulSoup is easy to learn and use. It handles messy HTML gracefully.
It integrates well with requests and pandas. It is beginner-friendly yet powerful. This makes it a top choice for scraping tasks.