How does an ETL pipeline process raw data into analytics-ready data?

An ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline is a structured
data workflow that collects information from multiple sources, processes it,
and stores it in a centralized system such as a data warehouse or data lake.
Key stages of an ETL pipeline:
- Extract – gathers raw data from databases, APIs, or files
- Transform – cleans, validates, aggregates, and formats data
- Load – stores processed data into a warehouse or lake
The transformation phase plays a critical role in ensuring
data quality and consistency. ETL pipelines are often scheduled to run at
fixed intervals, making them ideal for batch processing and reporting tasks.
Why ETL pipelines are important:
- Provide clean and reliable datasets for analytics
- Reduce manual data handling errors
- Ensure consistent data formats across systems
- Support business intelligence and decision-making
Real-life example:
In an e-commerce company, sales data may come from the website, mobile app,
and payment gateways. An ETL pipeline extracts this data daily, cleans
duplicates, converts currencies, and loads it into a data warehouse.
Analysts then use this data to track sales trends and customer behavior.
Modern tools such as Apache Airflow and AWS Glue
help automate and monitor ETL workflows efficiently.
Explain how data partitioning improves big-data system performance.
Partitioning is a data optimization technique that divides
large datasets into smaller, manageable segments based on keys such as
date, region, or category. This structure allows systems to process only
the relevant data instead of scanning the entire dataset.
Why partitioning is important:
- Significantly reduces the amount of data scanned during queries
- Improves query performance and response time
- Enhances parallel processing across compute nodes
- Lowers storage and compute costs in large-scale systems
Distributed data platforms such as Apache Spark,
Apache Hive, and Google BigQuery rely
heavily on partitioning to optimize data processing and job execution.
A well-designed partitioning strategy ensures efficient workload
distribution, faster analytics, and better scalability in modern
big data and cloud-based systems.
How does a distributed file system like HDFS store and manage big data?
A distributed file system, such as HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System),
is designed to store and manage very large datasets across multiple machines.
Instead of keeping a file on a single system, it spreads the data across a cluster.
How a distributed file system works:
- Large files are broken into smaller fixed-size blocks
- Blocks are distributed across many computers (nodes)
- Each block is stored multiple times to ensure fault tolerance
- A master node tracks where data blocks are located
- Worker nodes actually store and process the data
This design ensures high availability and reliability. Even if one machine
fails, the system continues working using the replicated data stored elsewhere.
Real-life example:
Imagine a very large book split into pages and stored in multiple lockers.
Each important page is kept in more than one locker. If one locker breaks,
the book can still be read using the remaining copies. HDFS works in a
similar way to protect and manage big data.
Explain the workflow of real-time data streaming with Apache Kafka.
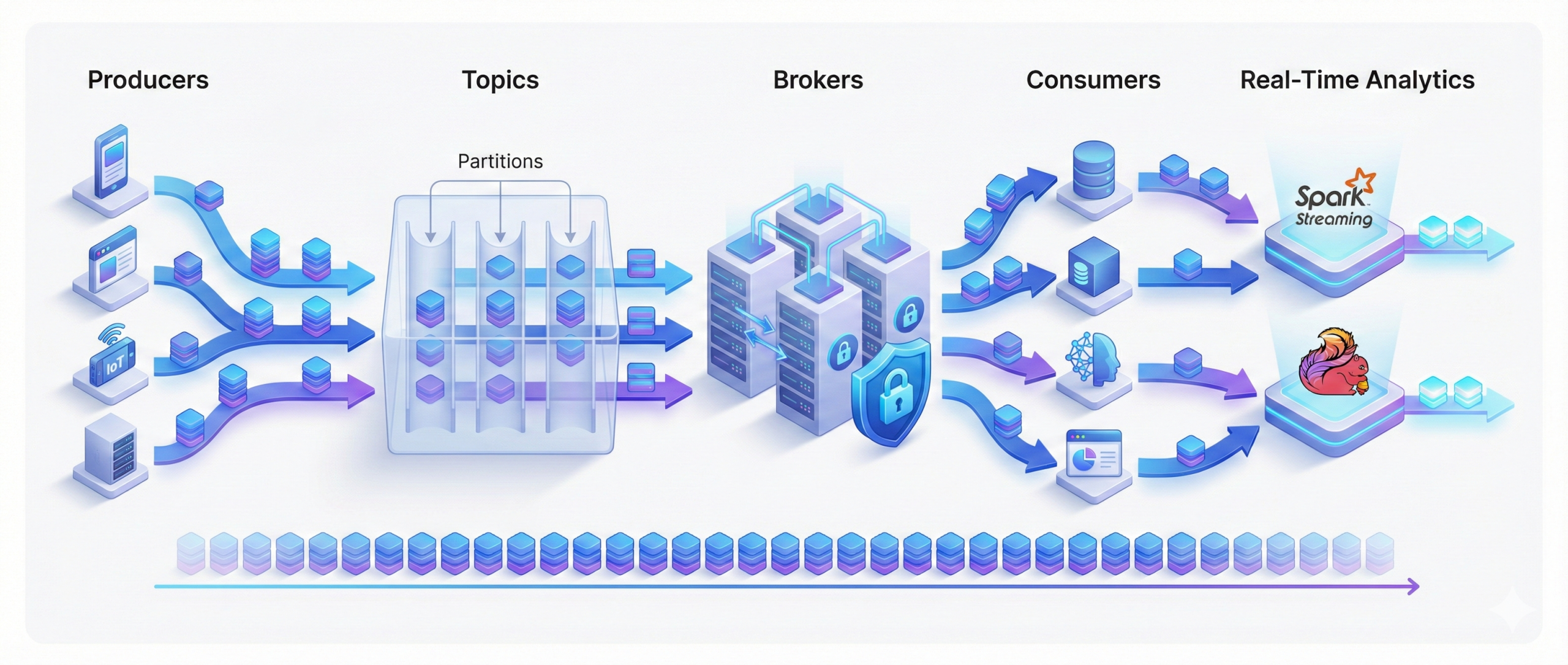
Kafka streams data through producers that write events into topics, which
are divided into partitions to enable parallel processing. Consumers read
records independently at their own pace, while brokers ensure data durability
and fault tolerance.
This decoupled and high-throughput design makes Kafka ideal for real-time
data pipelines. It integrates seamlessly with tools like Spark Streaming
and Flink to support real-time analytics and event-driven systems.
Kafka’s log-based architecture guarantees ordered and persistent data
streams, allowing systems to replay events reliably whenever needed.
Compare ETL and ELT pipelines.
| Feature | ETL (Extract–Transform–Load) | ELT (Extract–Load–Transform) |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Transform before loading | Transform inside warehouse |
| Best For | Traditional warehouses | Cloud-native analytics |
| Speed | Slower for large datasets | Faster using distributed SQL |
| Tools | Informatica, Talend | Snowflake, BigQuery |
ETL focuses on cleaning and transforming data before it is stored,
which works well for systems with fixed schemas and strict validation rules.
ELT takes advantage of modern cloud warehouses by loading raw data
first and transforming it later using powerful compute resources.
Key practical points:
- ETL prioritizes data quality before storage
- ELT prioritizes speed and flexibility
- ETL suits legacy and on-premise systems
- ELT scales better with big data and analytics workloads
Real-life examples:
ETL example:
A bank processes transaction data overnight. It validates records, removes
duplicates, and applies compliance rules before loading the data into a
reporting warehouse. This ensures accurate financial reports every morning.
ELT example:
An e-commerce company collects massive clickstream data. Raw events are first
loaded into Snowflake, and different teams later transform the same data for
sales analysis, marketing insights, and recommendation models.
Compare Data Warehouses and Data Lakes.
| Feature | Data Warehouse | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured | All types (raw) |
| Schema | Schema-on-write | Schema-on-read |
| Use Case | BI, reporting | ML, raw ingestion |
| Storage Cost | Higher | Lower |
Warehouses deliver clean, structured data for analytics, while lakes store raw,
flexible data for exploration and machine learning.
Real-life example:
A company stores monthly sales summaries in a data warehouse for management
reports, while keeping raw logs, images, and clickstream data in a data lake
for future machine learning experiments.
What are the differences between batch processing and stream processing?
| Aspect | Batch Processing | Stream Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Arrival | Periodic | Continuous |
| Latency | High | Low |
| Use Cases | ETL jobs, reports | Real-time analytics |
| Tools | Hadoop, Airflow | Kafka, Flink, Spark Streaming |
Batch processing is suitable for analyzing large volumes of historical data,
while stream processing handles data instantly as it is generated.
Real-life example:
A company generates daily sales reports using batch processing at night,
while the same company uses stream processing to monitor live website traffic
and trigger alerts when unusual activity occurs.
Compare SQL and NoSQL databases for data engineering tasks.
| Feature | SQL Databases | NoSQL Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Schema | Fixed | Flexible |
| Scalability | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Use Case | ACID, structured data | Big data, distributed apps |
| Examples | MySQL, PostgreSQL | MongoDB, Cassandra |
SQL databases focus on strong consistency and structured data,
while NoSQL databases are designed to scale easily and handle
large volumes of distributed data.
Real-life example:
A banking system uses an SQL database to manage transactions where
accuracy and consistency are critical, while a social media platform
uses a NoSQL database to store user posts and activity that grow rapidly
across millions of users.
Why is data modeling important in data engineering?
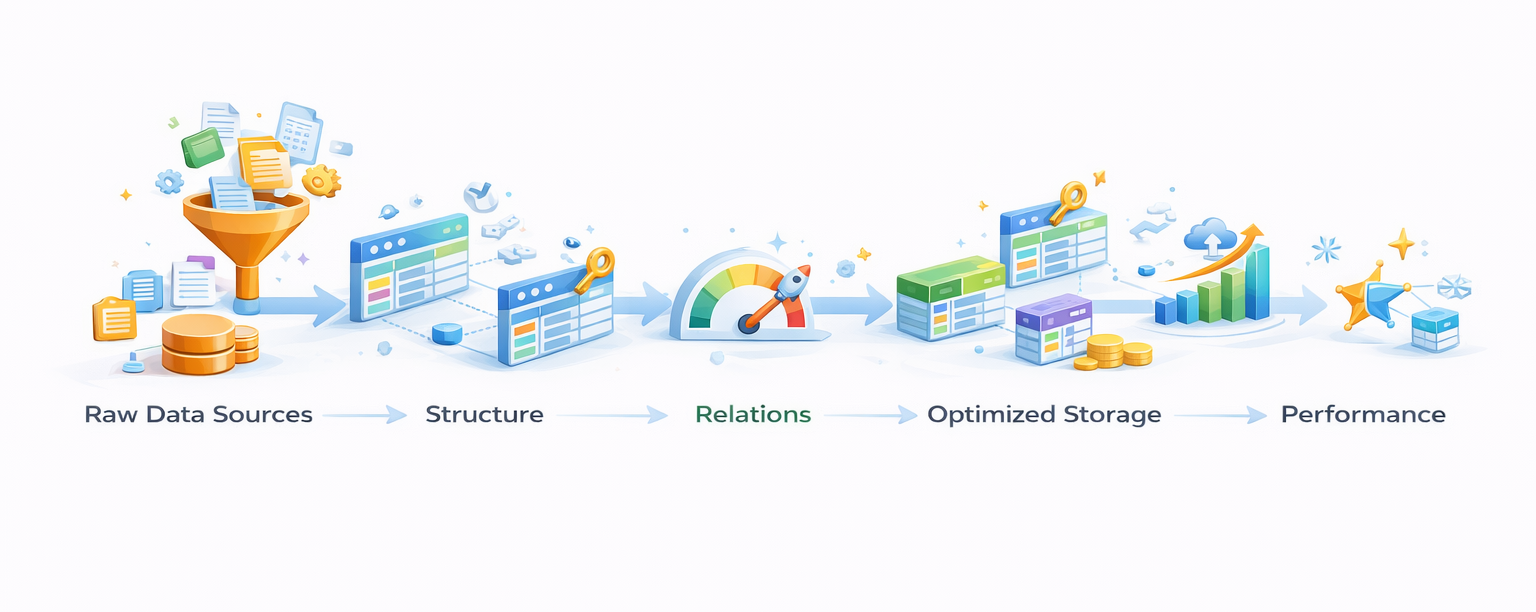
Data modeling defines the structure, relationships, and rules
used to organize data. A well-designed model maintains consistency across
systems, minimizes redundancy, and improves query performance. It also
supports scalable analytics as data volumes grow. Common warehouse designs
include star and snowflake schemas.
Real-life example:
An e-commerce company designs a data model where customers, products, and
orders are clearly related. This allows analysts to quickly answer questions
like “top-selling products” or “monthly revenue” without scanning unnecessary
data.
What is data lineage, and why is it critical?
Data lineage describes how data flows through a system,
starting from ingestion, moving through transformations, and finally
reaching storage or analytics layers. It shows where data comes from,
how it changes, and where it is used.
Why data lineage is critical:
- Helps trace errors by identifying where data was modified
- Improves transparency across complex data pipelines
- Supports compliance in regulated industries
- Builds trust in dashboards and analytics results
- Makes impact analysis easier before making changes
Many organizations rely on tools such as Apache Atlas
and Collibra to automatically capture and visualize
data lineage across systems.
Real-life example:
If a finance report suddenly shows incorrect revenue numbers, data lineage
helps teams trace the issue back to a specific transformation or source file,
allowing quick correction without guessing where the problem occurred.
What is schema evolution in big-data systems?
Schema evolution allows datasets to change structure without breaking
existing pipelines. Formats like Avro, Parquet, and ORC support backward
and forward compatibility.
This flexibility is essential for continuously changing business
requirements. Schema evolution enables safe updates to fields, types,
and metadata.
It also simplifies long-term data storage in data lakes.
Real-life example:
An e-commerce company adds a new column for discount information to its
order data. With schema evolution, older datasets continue to work
without modification, while new records safely include the additional
field.
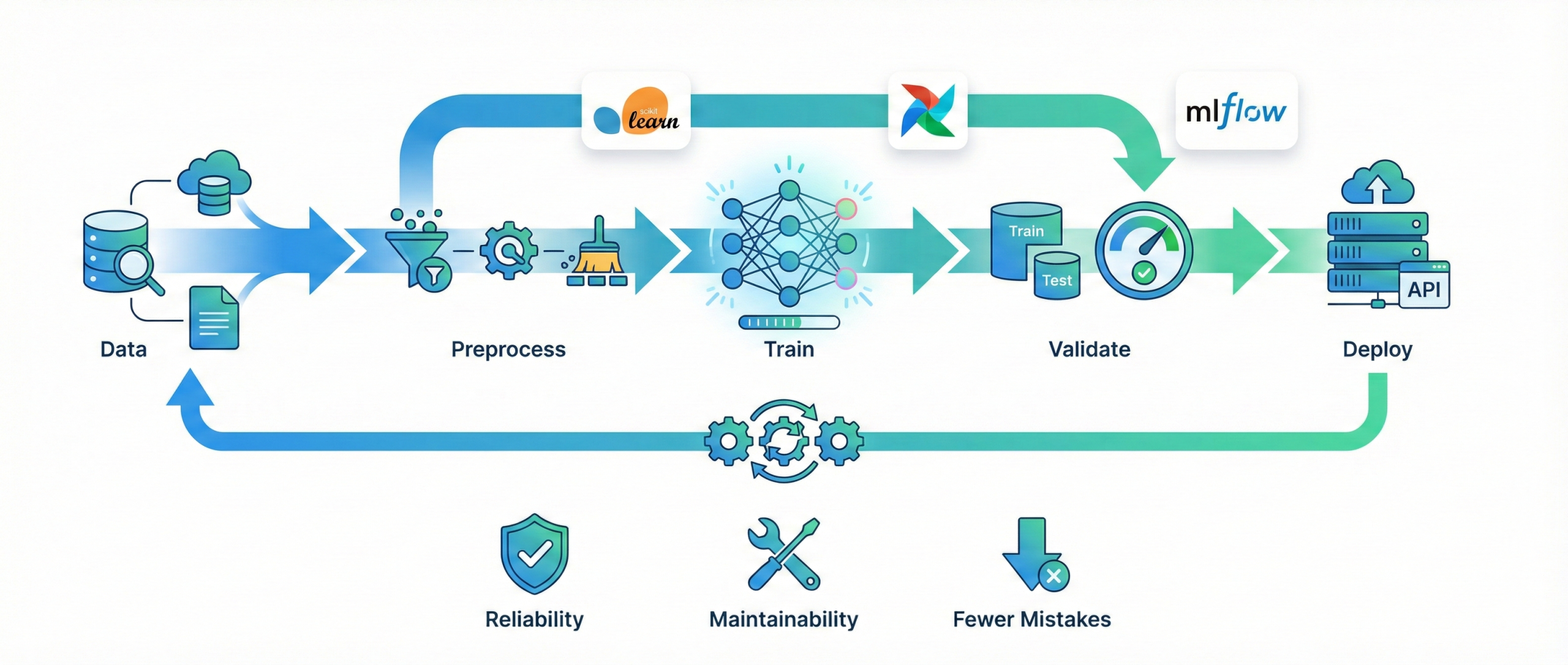
How does Spark optimize large-scale data processing?
Apache Spark uses in-memory computation to significantly
accelerate data processing compared to traditional disk-based systems.
This allows Spark to handle large-scale analytics and machine learning
workloads efficiently.
Key features that make Spark powerful:
- In-memory processing for faster execution
- DAG scheduler that optimizes execution paths
- Catalyst optimizer for efficient SQL query planning
- Tungsten engine for better CPU and memory utilization
Together, these features make Spark well-suited for processing large
datasets, real-time analytics, and machine learning pipelines.
Real-life example:
A telecom company analyzes billions of call records daily. Using Spark,
it keeps data in memory while computing usage patterns and detecting
network issues, delivering insights in minutes instead of hours.
Why is orchestration important in data pipelines?
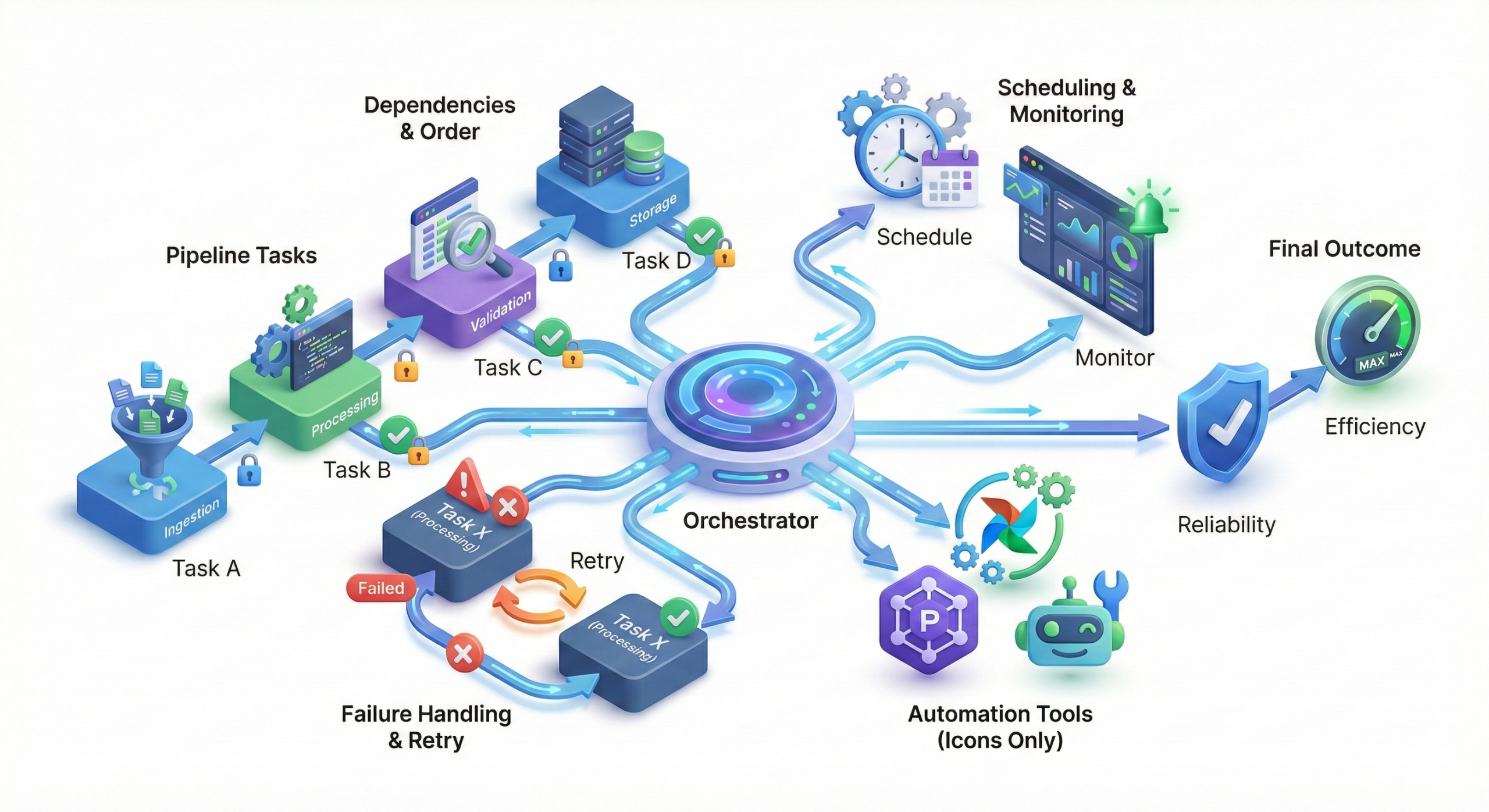
Data pipelines consist of multiple dependent tasks requiring coordination.
Orchestration tools ensure jobs run in the correct order and handle failures
automatically.
They also provide scheduling, monitoring, and retry logic. Tools like
Airflow, Prefect, and Luigi
automate complex workflows.
Orchestration ensures reliability and efficiency in production environments.
Real-life example:
In a retail company, sales data must be ingested, cleaned, aggregated, and
loaded into a dashboard every night. An orchestration tool ensures each step
runs only after the previous one succeeds and automatically retries tasks
if a server or network failure occurs.
What is the role of columnar storage formats in analytics?
Columnar formats such as Parquet and
ORC store data column by column instead of row by row.
This storage approach is optimized for analytics rather than transactions.
Why columnar storage is effective:
- Reduces storage size through efficient compression
- Reads only required columns instead of full rows
- Speeds up analytical queries significantly
- Works well with Spark, Hive, and cloud data warehouses
- Ideal for read-heavy data science workloads
Real-life example:
A business intelligence team runs daily reports on sales data containing
hundreds of columns. Using Parquet, queries scan only revenue and date
columns instead of the entire dataset, reducing query time from minutes
to seconds.
What is data sharding, and when is it used?
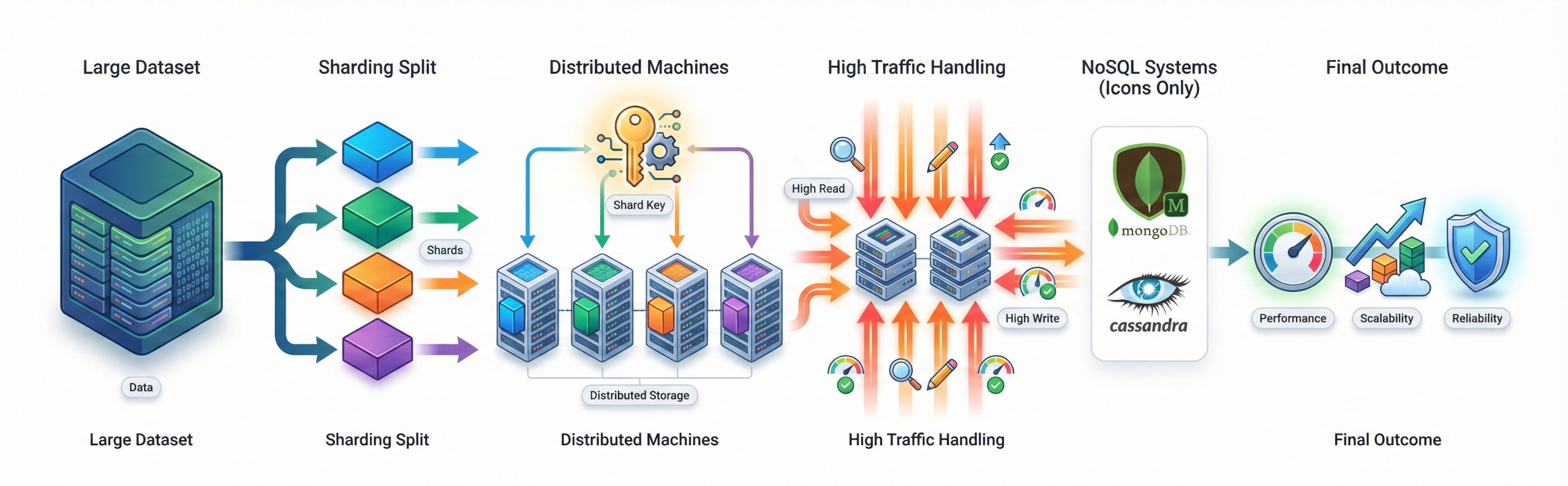
Sharding is a database scaling technique that splits a large
dataset horizontally across multiple machines. Instead of storing all data
on a single server, each shard holds a portion of the data.
Why sharding is used:
- Improves scalability for large datasets
- Distributes read and write traffic across servers
- Prevents a single database from becoming a bottleneck
- Supports high-traffic and data-intensive applications
Choosing the right shard key is critical. A well-designed
key ensures even data distribution and balanced load across shards.
Sharding is widely used in NoSQL systems such as MongoDB and Cassandra.
Real-life example:
A social media platform stores user data by user ID across multiple shards.
As millions of users post content simultaneously, sharding allows the
system to handle high traffic smoothly without slowing down any single server.
Why are workflow metadata and monitoring essential in data engineering?
Metadata and monitoring are essential for understanding
how data pipelines work and how well they perform. Metadata explains
what the pipeline is doing, while monitoring shows how it behaves in
real time.
Why metadata and monitoring matter:
- Describe pipeline tasks, data sources, schemas, and dependencies
- Track runtime statistics such as execution time and success rates
- Detect failures and performance bottlenecks quickly
- Improve reliability and transparency across workflows
- Help teams debug issues and optimize resource usage
Modern platforms such as Airflow and Datadog
automate workflow observability by collecting metadata and providing
dashboards, alerts, and logs.
Real-life example:
In a data team generating daily business reports, monitoring alerts
engineers when a pipeline suddenly fails or slows down. Metadata then
helps identify which task, table, or schema change caused the issue,
allowing faster fixes and minimal impact on reporting.
What are the advantages of Parquet over CSV for data science workloads?
Parquet is a columnar storage format that compresses data
efficiently and stores it in a binary layout. It is designed specifically
for analytical workloads.
Why Parquet is widely used:
- Stores data by columns, not rows, improving scan performance
- Uses strong compression to reduce storage size
- Supports predicate pushdown to read only required data
- Preserves schema and data types, unlike CSV files
- Integrates smoothly with Spark, Hive, and cloud storage
Because queries read only relevant columns instead of entire rows,
Parquet significantly speeds up analytics and reporting jobs.
Real-life example:
A data analytics team stores customer transactions in Parquet format.
When running a report on monthly revenue, the query reads only the
date and amount columns instead of scanning the full dataset, cutting
query time from minutes to seconds.
What is data deduplication, and why is it needed?
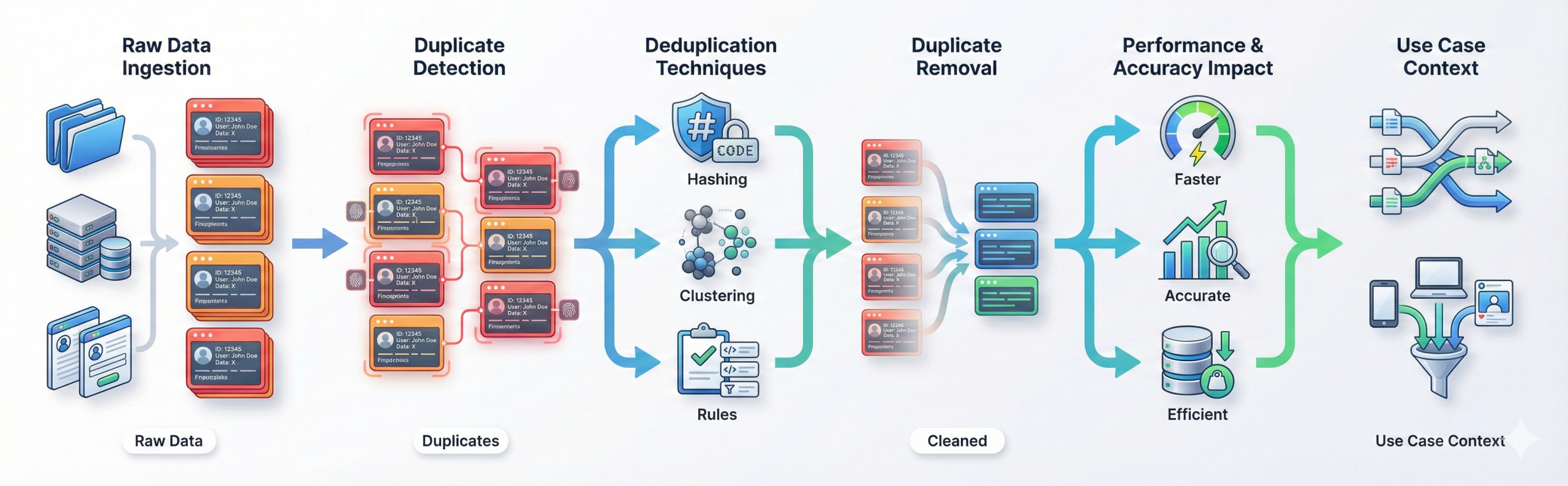
- Deduplication removes repeated records to ensure accuracy and reduce storage.
- Duplicate data skews analytics and increases processing time.
- Techniques include hashing, clustering, and rule-based checks.
- Deduplication is crucial for merged data sources or user-generated inputs.
- Clean datasets improve model training and reporting quality.
Real-life example:
When customer data is collected from a website and a mobile app, the same
user may appear multiple times. Deduplication ensures each customer is stored
once, resulting in accurate reports and better analytics.
Explain the role of message queues in data engineering.
Message queues play a key role in data engineering by
separating data producers from consumers. This decoupling makes systems
more scalable, reliable, and easier to maintain.
Why message queues are important:
- Decouple producers and consumers to reduce system dependency
- Buffer incoming data during traffic spikes
- Ensure reliable delivery of messages and events
- Enable asynchronous processing across services
- Support microservice communication and event-driven design
Technologies such as Kafka, RabbitMQ,
and AWS SQS are commonly used to handle high-volume
event ingestion and streaming workloads.
Real-life example:
In an e-commerce platform, every user action—such as placing an order
or adding an item to a cart—is sent to a message queue. Multiple services
then consume these messages independently to update inventory, trigger
notifications, and generate analytics without slowing down the website.
How does caching improve data pipeline performance?
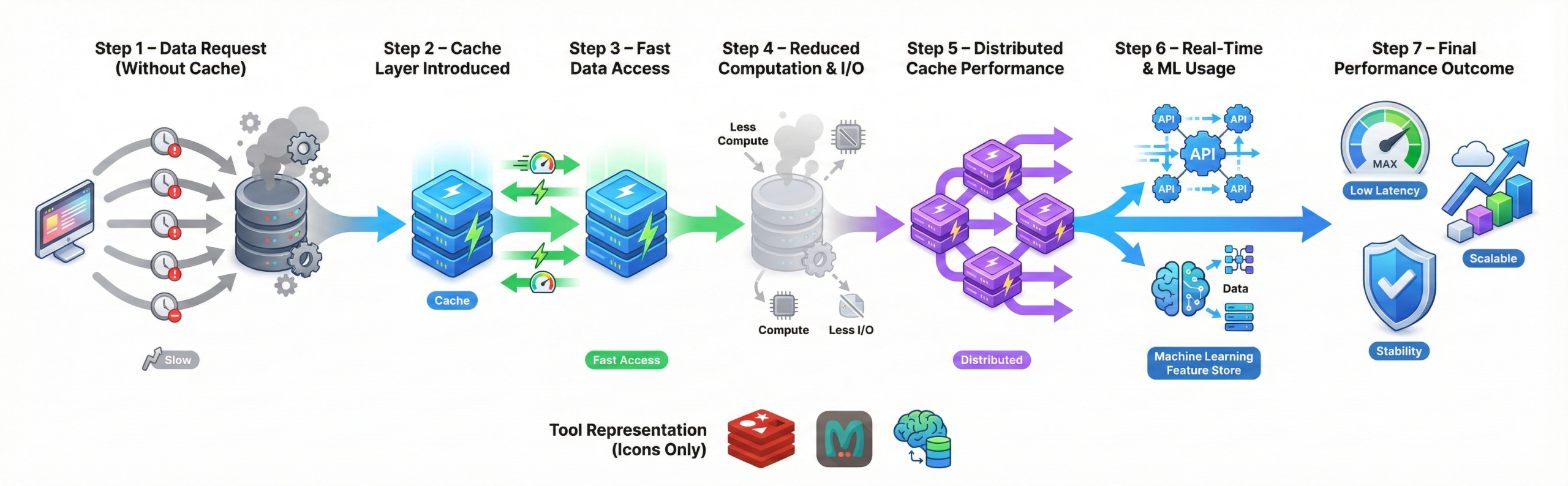
Caching stores frequently accessed data in high-speed memory. This
significantly reduces repeated computation and I/O operations.
Distributed caches like Redis and Memcached accelerate real-time
pipelines. Caching is especially useful in API systems and ML
feature retrieval.
It ensures low latency and improved scalability.
Real-life example:
A food delivery app caches restaurant menus in Redis so repeated user
requests load instantly instead of hitting the database every time.










