What is Ethical Hacking?

Ethical hacking is the legal practice of identifying security weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
- Identifies vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications
- Performed with official permission from the organization
- Uses a structured methodology:
- Reconnaissance
- Scanning
- Exploitation
- Post-Exploitation
- Reporting
- Improves overall security and protects sensitive data
- Fully legal, controlled, and documented process
What is the CIA Triad and why is it important?
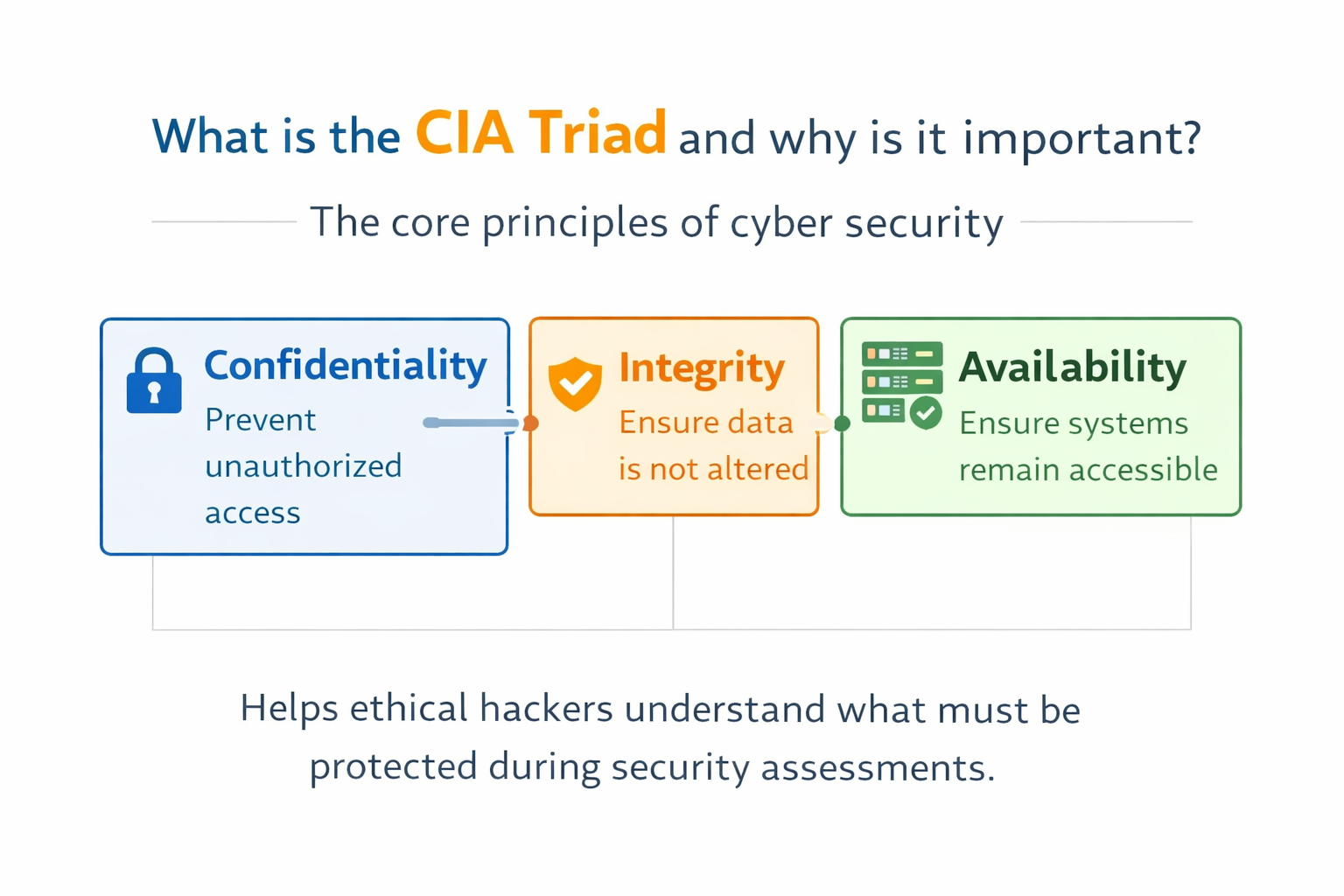
The CIA Triad represents
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability — the core principles of cyber security.
It ensures that data remains protected, accurate, and available to authorized users.
- Confidentiality → Prevent unauthorized access
- Integrity → Ensure data is not altered
- Availability → Ensure systems remain accessible
This model helps ethical hackers understand what must be protected during security assessments.
What is the difference between Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking?
| Feature | Cyber Security | Ethical Hacking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Defend systems | Find weaknesses |
| Role | Prevention | Authorized testing |
| Approach | Defensive | Offensive (legal) |
| Tools | Firewalls, IDS, Antivirus | Nmap, Burp Suite, Metasploit |
| Goal | Protect the organization | Strengthen the organization |
This table clearly shows why both fields are essential and connected.
What is Malware? Explain its types.
Malware refers to malicious software intentionally created to damage systems,
steal sensitive information, or misuse data without the user’s knowledge.
It is one of the most common tools used in cyber attacks.
Common types of malware include:
- Virus – Attaches to files or programs and spreads when they are executed
- Worm – Spreads automatically across networks without user interaction
- Trojan – Appears legitimate but secretly contains malicious code
- Ransomware – Encrypts or locks files and demands payment for access
- Spyware – Silently monitors user activity and collects confidential information
Understanding different malware types helps beginners recognize real-world attack patterns
and take appropriate security measures.
What is an IP Address and why is it important in hacking?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical identifier
assigned to every device connected to a network. It allows devices to locate, identify,
and communicate with each other over the internet or a local network.
Ethical hackers use IP addresses to:
- Identify the target system or device
- Perform network scanning and enumeration
- Detect open ports and running services
- Understand the overall network structure
Without IP addresses, no network-based testing or hacking activity can begin,
as there would be no way to locate or communicate with a target system.
What is Port Scanning? Why do hackers scan ports?
Port scanning is the process of checking a system or network to find
which ports are open and which services are running on them. Each open port
acts as a possible entry point into a system.
Hackers and ethical hackers scan ports to identify:
- Outdated or vulnerable services
- Weak or misconfigured services
- Unauthorized or unnecessary applications
Tools such as Nmap are commonly used to perform port scanning and
identify potential attack vectors before exploiting system weaknesses.
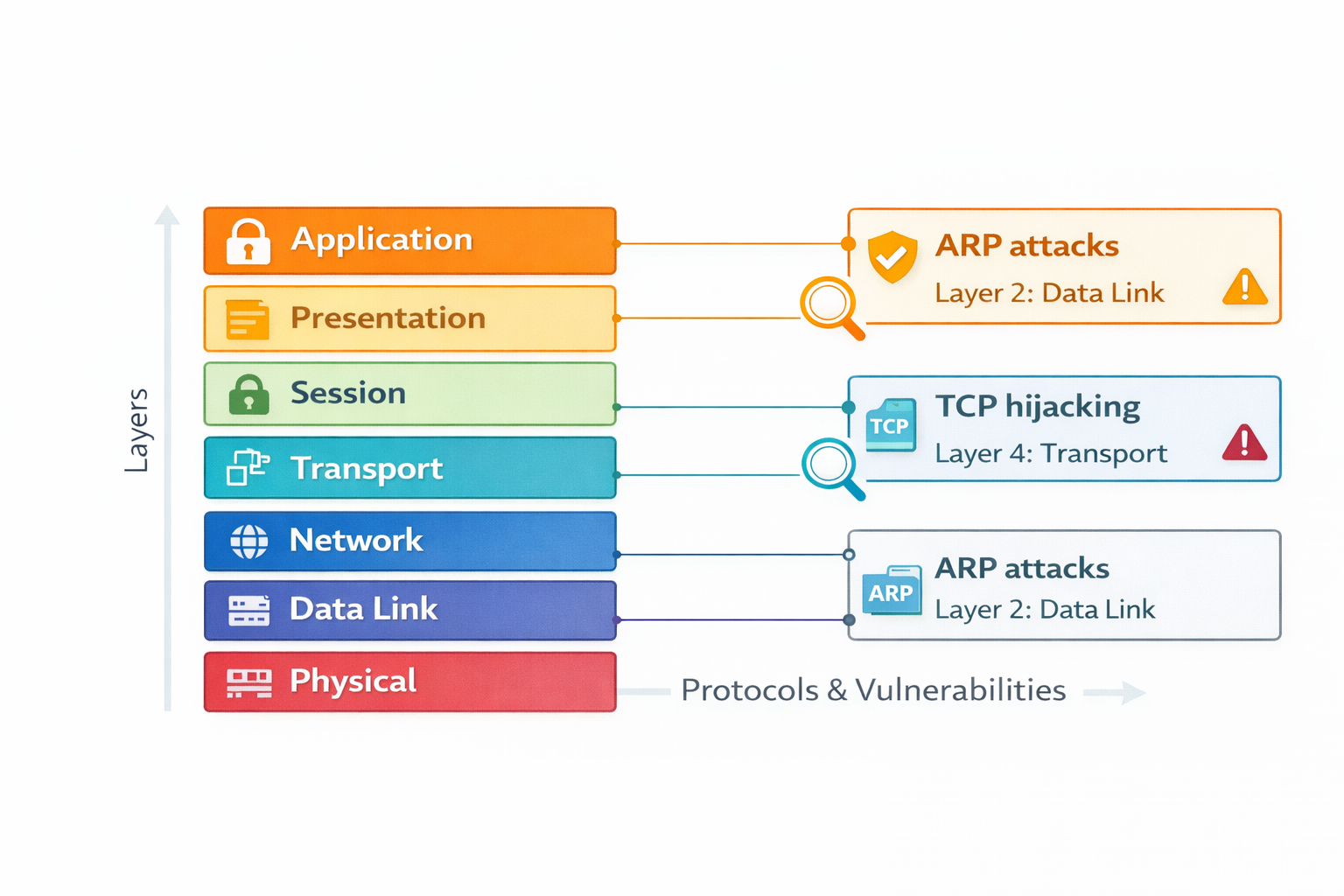
What is the OSI Model?
The OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection Model) is a
7-layer framework that explains how data travels from one device
to another across a network. It provides a structured way to understand
communication processes and network behavior.
In ethical hacking, the OSI Model helps security professionals
identify vulnerabilities at specific layers.
For example, ARP attacks occur at
Layer 2 (Data Link), while
TCP hijacking targets
Layer 4 (Transport).
The seven layers of the OSI Model are:
- Physical
- Data Link
- Network
- Transport
- Session
- Presentation
- Application
What is Subnetting? Why is it used?
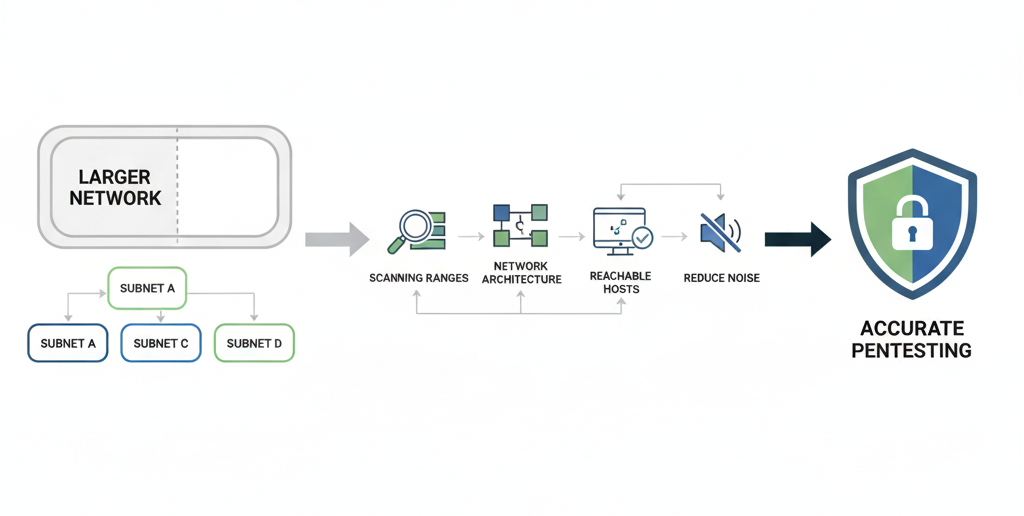
Subnetting is the process of dividing a large network into
smaller and more efficient sub-networks. It helps improve network
organization, performance, and security.
In ethical hacking, subnetting helps professionals to:
- Understand scanning ranges more accurately
- Analyze the overall network architecture
- Identify reachable and active hosts
- Reduce unnecessary noise during reconnaissance
Subnetting is essential for performing accurate and efficient
penetration testing on modern networks.
What is Reconnaissance? Why is it the first step in hacking?
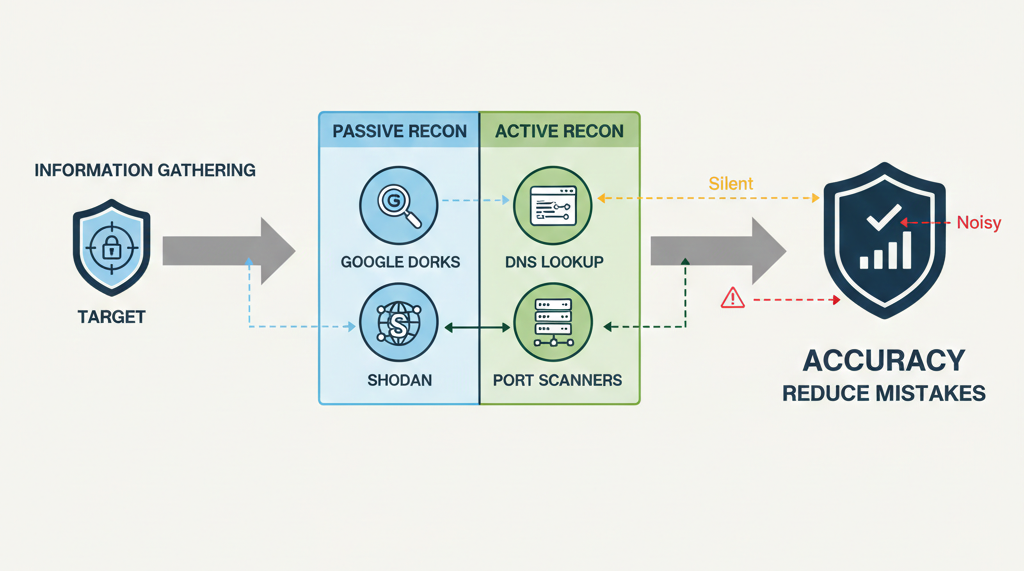
Reconnaissance is the process of collecting information about a target
using both passive and active techniques. It helps ethical hackers understand
the target environment before attempting any attack.
During reconnaissance, ethical hackers commonly use:
- Google Dorks
- WHOIS
- Shodan
- DNS lookup tools
- Port scanners
Effective reconnaissance reduces mistakes, improves attack accuracy,
and increases the success rate of security assessments.
What is WHOIS and how is it used in ethical hacking?
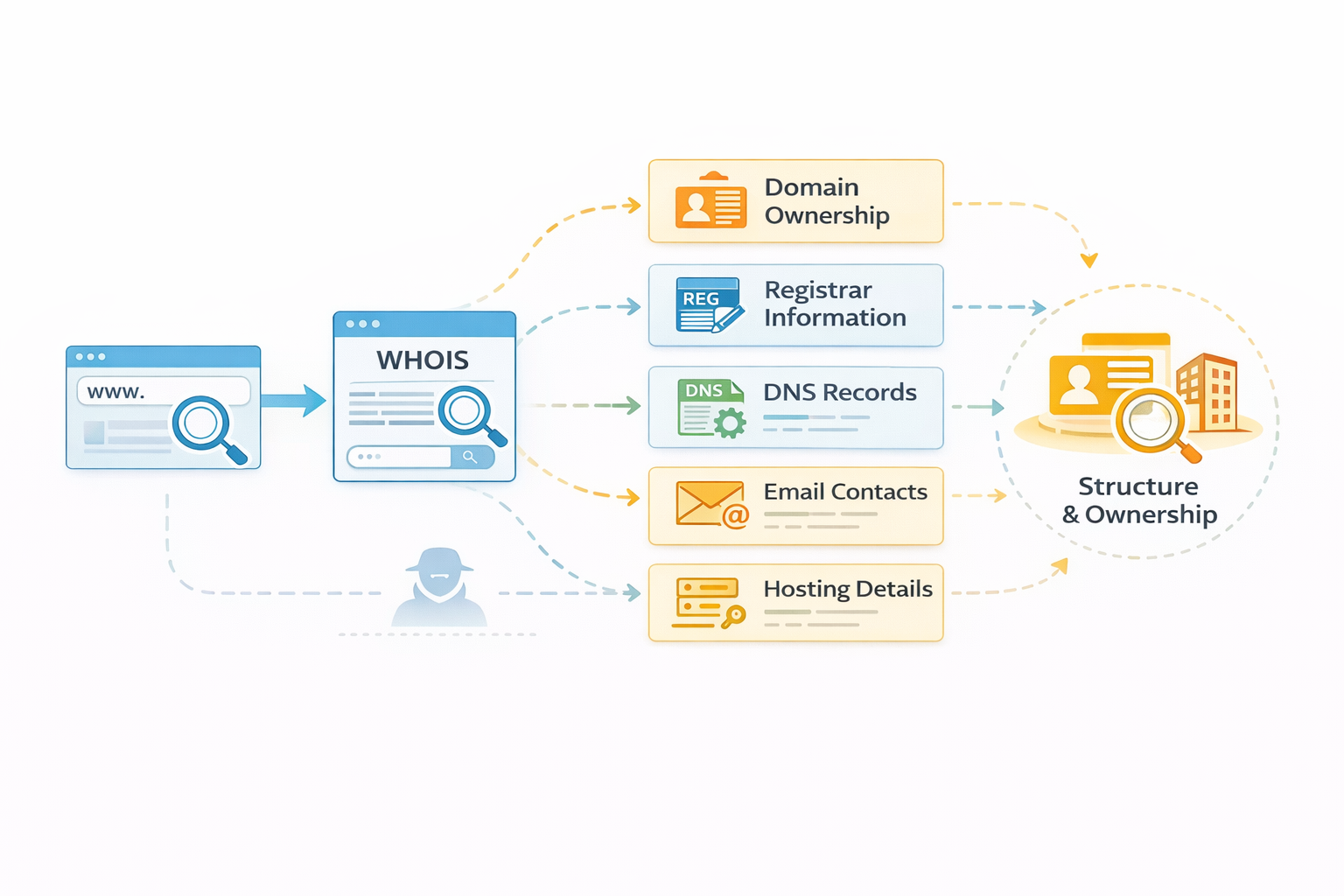
WHOIS is a query tool used to retrieve important information about
a domain name, including domain ownership details, registrar information,
DNS records, email contacts, and hosting data.
Ethical hackers use WHOIS during
passive reconnaissance to understand the structure and ownership
of a website without directly interacting with the target system,
making it a safe and stealthy information-gathering technique.
What is the difference between Virus, Worm, and Trojan?
| Feature | Virus | Worm | Trojan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spread Method | Needs user action | Spreads automatically | Disguised as legitimate |
| Damage | Corrupts data/files | Network overload | Steals information |
| Execution | Attaches to files | Self-replicates | Requires installation |
This comparison helps beginners quickly understand malware behavior differences.
What is a Firewall?
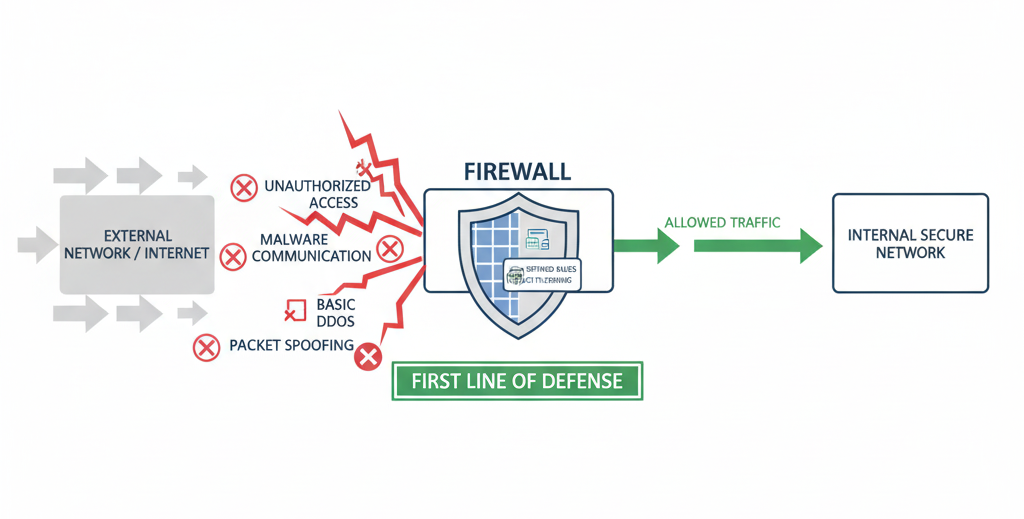
A firewall is a security device or software that monitors and filters
incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules.
It acts as a protective barrier between trusted and untrusted networks.
A firewall helps prevent:
- Unauthorized access
- Malware communication
- Basic-level DDoS attacks
- Packet spoofing
Firewalls are considered the first line of defense
in securing networks and systems.
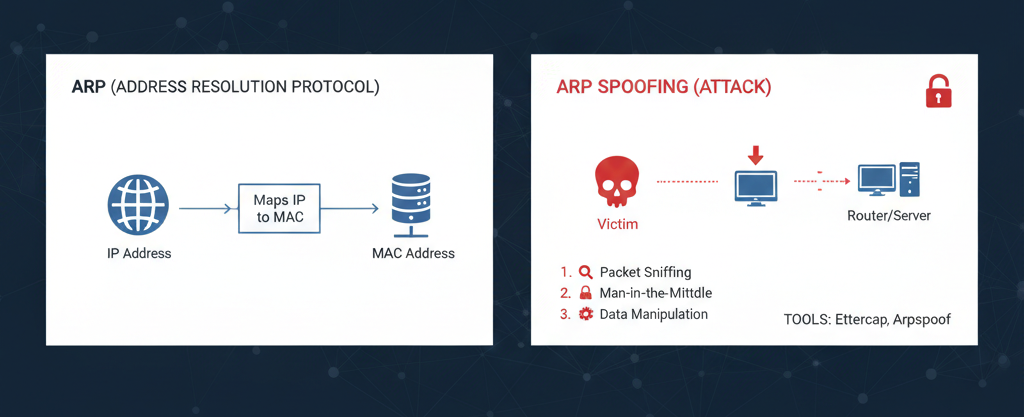
What is ARP and ARP Spoofing?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to map IP addresses
to MAC addresses within a local network.
ARP Spoofing is an attack technique in which an attacker sends
fake ARP messages to associate their MAC address with a legitimate IP address,
causing network traffic to be redirected through the attacker’s machine.
ARP spoofing enables attackers to perform:
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
- Packet sniffing
- Data manipulation
Common tools used for ARP spoofing include
Ettercap and Arpspoof.
What is Password Cracking? Explain basic methods.
Password cracking is the process of attempting to recover
passwords by systematically testing possible combinations or known patterns.
Common password cracking techniques include:
- Brute Force – tries every possible combination
- Dictionary Attacks – uses a predefined wordlist
- Hybrid Attacks – combines brute force and dictionary methods
- Rainbow Tables – uses precomputed hash lookups
Ethical hackers perform password cracking to evaluate password strength
and identify weak authentication mechanisms.
What is SQL Injection? Why is it dangerous?
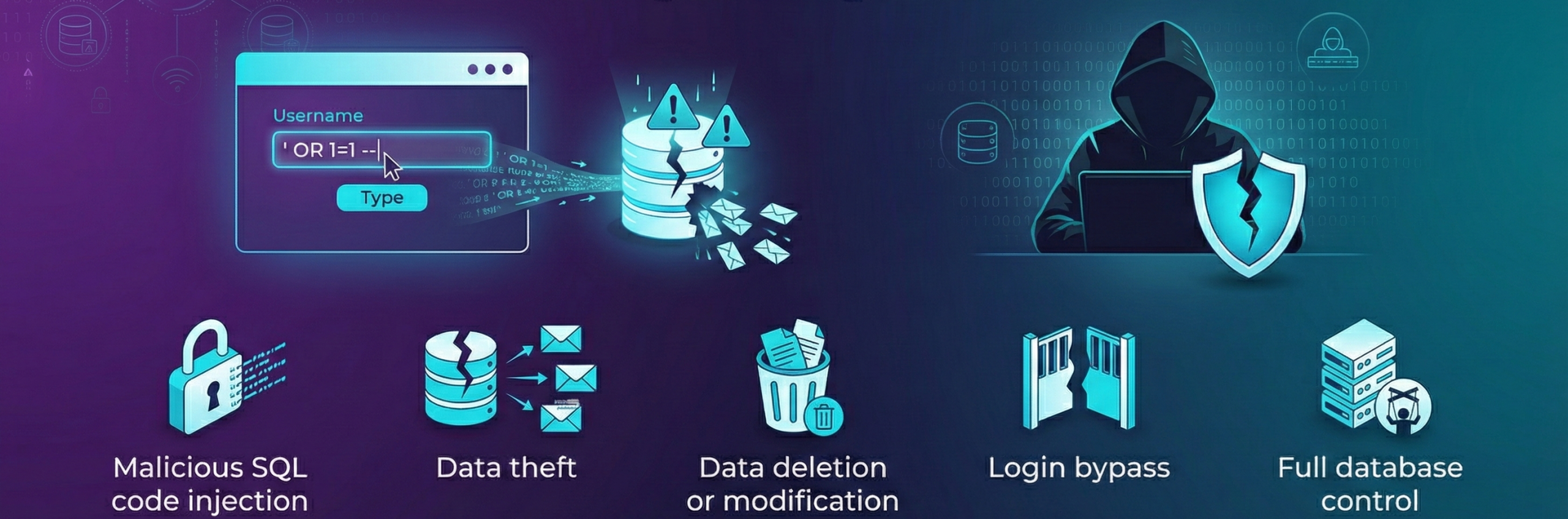
SQL Injection is a web-based attack in which attackers insert
malicious SQL code into input fields to gain unauthorized access to
or manipulate database data.
SQL Injection attacks can:
- Reveal usernames and passwords
- Delete or modify database records
- Bypass authentication and login systems
- Gain control over the database server
SQL Injection is considered one of the
most critical vulnerabilities listed by OWASP.
What is a Honeypot?
A honeypot is a decoy system or resource intentionally designed
to attract attackers and monitor their activities. It mimics real systems
to study attacker behavior without risking critical assets.
Organizations use honeypots to:
- Identify the origin of attacks
- Capture and analyze malware
- Study new hacking techniques and tools
- Distract attackers away from real systems
A honeypot acts like a controlled trap that helps security teams
detect, mislead, and monitor intruders in a safe environment.
What is Encryption? Why is it important?

Encryption converts readable data into unreadable
ciphertext, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected
from unauthorized access.
Encryption helps protect:
- Passwords
- Payment data
- Personal information
- Business secrets
Even if hackers intercept encrypted data, they cannot read it
without the correct decryption key.
What is Social Engineering?
Social Engineering is an attack technique that manipulates
people into revealing confidential or sensitive information rather than
exploiting technical weaknesses.
Common social engineering examples include:
- Phishing emails
- Fake login pages
- Impersonation
- Pretexting
Human weaknesses are often easier to exploit than technical
vulnerabilities, making social engineering highly effective.
What is a DDoS Attack?
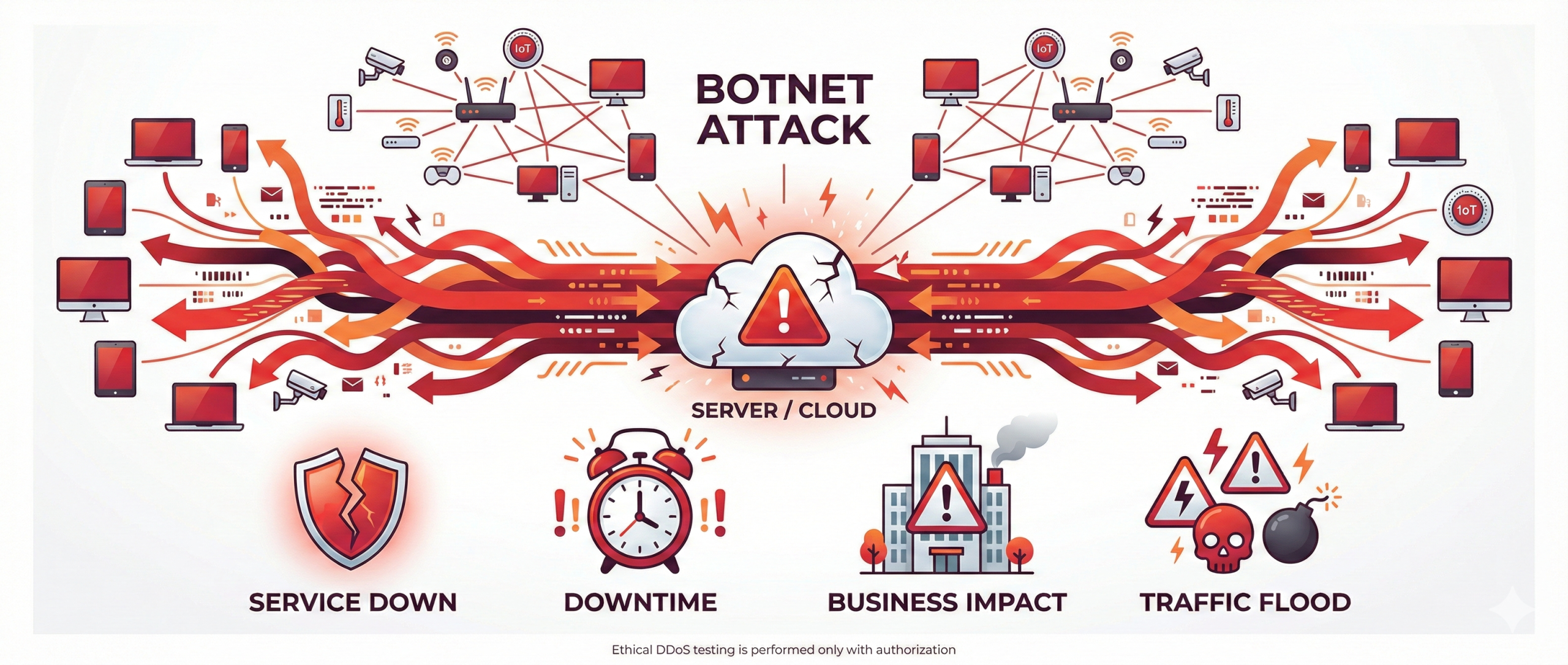
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack floods a server
or network with massive amounts of traffic from multiple compromised devices,
often called a botnet. This overload makes the service unavailable
to legitimate users.
Attackers perform DDoS attacks to:
- Crash online services
- Cause prolonged downtime
- Damage organizational reputation
- Interrupt normal business operations
Ethical hackers simulate DDoS scenarios only under
strict authorization to test system resilience
and improve defensive measures.
What is Sniffing? Explain with examples.
Sniffing is the process of capturing and analyzing network traffic
to inspect data packets as they travel across a network. Attackers and ethical
hackers use sniffing techniques to monitor communication between devices.
Hackers use sniffing to capture information such as:
- Usernames and passwords
- Session cookies
- Network protocol data
- API requests and responses
Common sniffing tools include Wireshark and Tcpdump.
Sniffing helps security professionals identify insecure communication
channels and detect data being transmitted without proper encryption.