Q1. What is Git, and how does it work internally?
Git is a distributed version control system used to track changes in code.
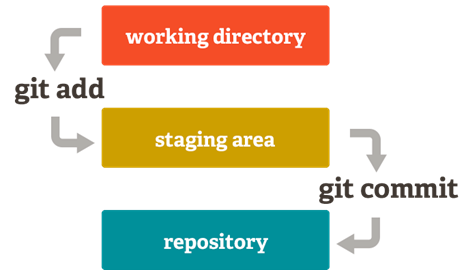
It works with three main areas: Working Directory, Staging Area, and Repository.
Developers modify files in the working directory and move selected changes to the staging area using git add.
When changes are ready, a commit saves a snapshot of those changes into the repository.
This workflow allows safe experimentation, proper version tracking, and easy rollback of previous changes.
Q2. What is a Git repository, and what does it contain?
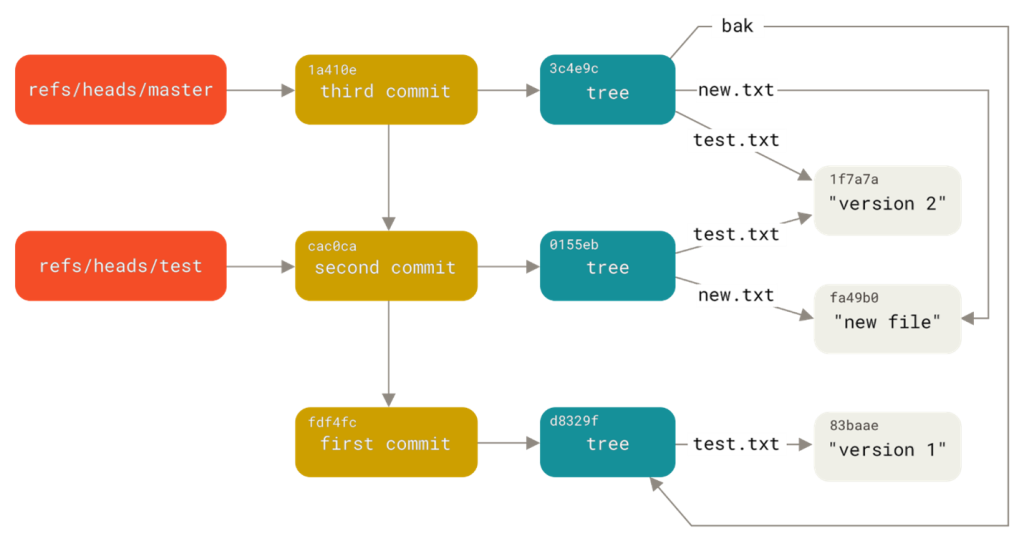
A Git repository stores all project versions and history. It contains commits, branches, tags, and configuration files.
The .git folder holds metadata and object storage. Each commit references a snapshot of files and previous commits.
This structure enables fast branching and merging.
Q3. How does branching work in Git?
Branches allow developers to work on features independently.
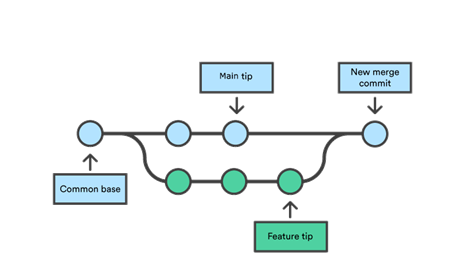
Each branch points to a specific commit. Git creates lightweight branches without copying files.
Once work is complete, branches are merged back into the main branch.
Branching supports parallel development and safer collaboration.
Q4. How does GitHub support collaboration in teams?
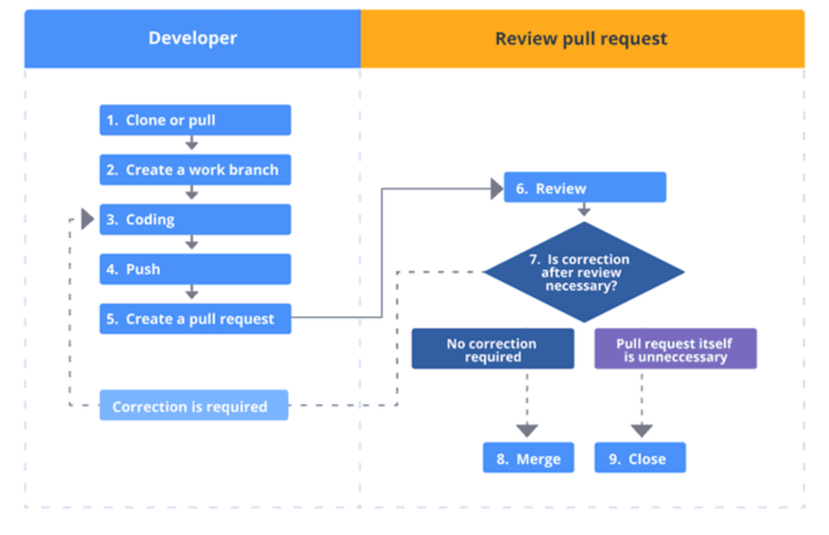
GitHub provides remote repositories for sharing code. Developers push changes and create pull requests.
Pull requests enable code review, discussion, and testing before merging. GitHub also tracks issues, commits, and contributors.
This makes team collaboration structured and transparent.
Q5. Difference between Git and GitHub
Git manages code history, while GitHub manages collaboration.
| Feature | Git | GitHub |
| Type | Version control tool | Hosting platform |
| Usage | Track code locally | Share code online |
| Internet | Not required | Required |
| Example | git commit | Pull request |
Q6. Difference between git clone and git pull
clone is for starting, pull is for syncing.
| Command | Purpose | When Used |
| git clone | Copy full repo | First time setup |
| git pull | Update local repo | Ongoing work |
| Data | Full repository | Latest changes |
| Frequency | Once | Many times |
Q7. Difference between git fetch and git pull
fetch is safer for reviewing changes before merging.
| Command | Action | Merges Changes |
| git fetch | Downloads updates | No |
| git pull | Fetch + merge | Yes |
| Safety | Safer | Risk of conflicts |
| Usage | Review first | Quick update |
Q8. Difference between public and private repositories
Private repos are preferred for company code.
| Feature | Public Repo | Private Repo |
| Visibility | Everyone | Selected users |
| Security | Low | High |
| Use Case | Open source | Company projects |
| Access Control | Limited | Full control |
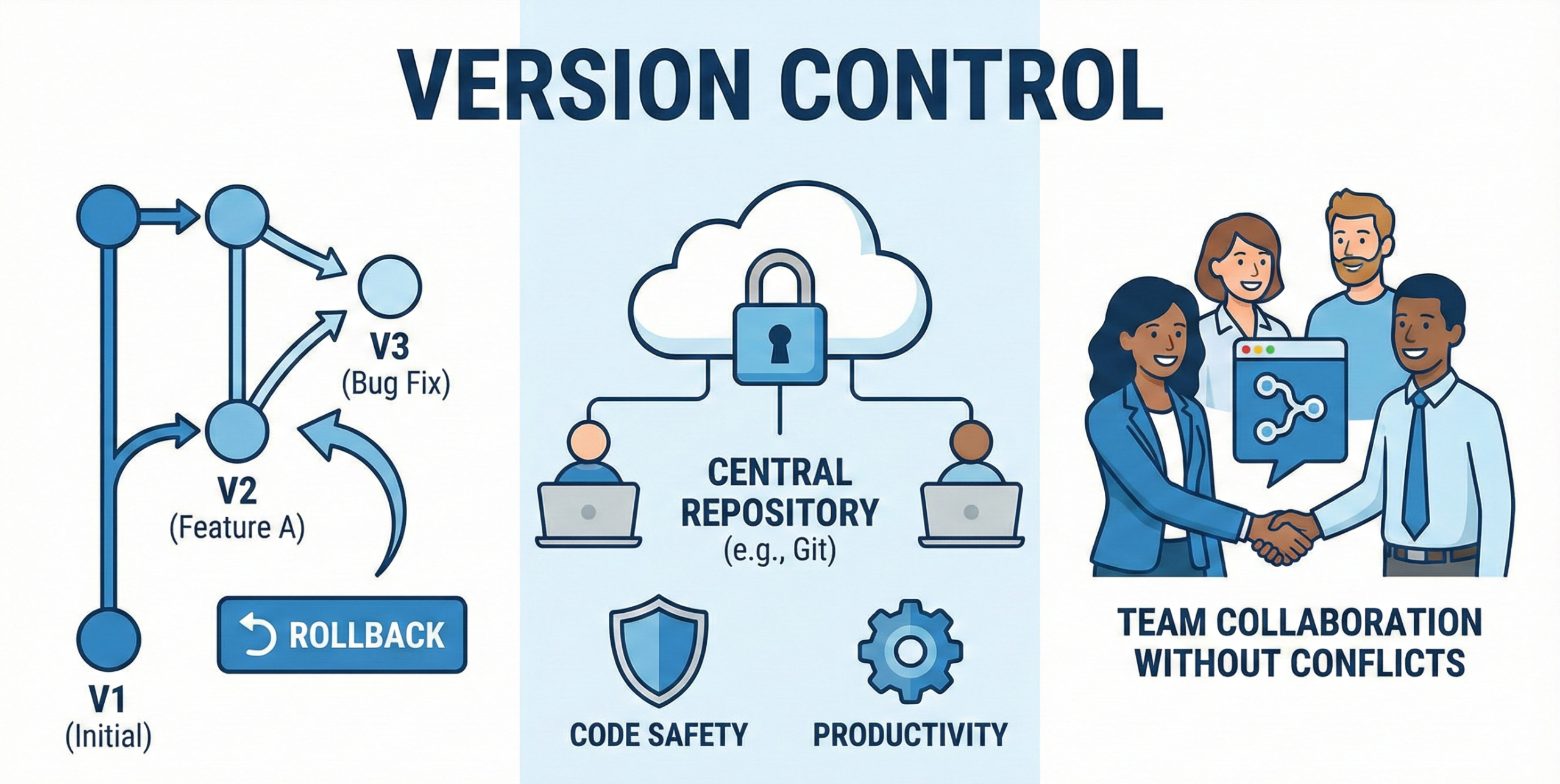
Q9. What is version control, and why is it important?
Version control tracks changes in code over time. It allows rollback to previous versions. It helps teams collaborate without conflicts.
Git is the most popular version control system today. It improves code safety and productivity.
Q10. What is a commit in Git?
A commit in Git is a saved snapshot of your project at a specific point in time.
Whenever you make changes and commit them, Git records those changes permanently in the repository history.
It helps you track what was changed, when it was changed, and who made the change.
Key Points:
- A commit stores the current state of tracked files.
- Each commit has a unique hash ID.
- It includes a commit message, author name, and timestamp.
- Commits create the project’s version history.
- Small and meaningful commits are considered best practice.
Example Situation:
- You fix a login bug → make a commit: “Fix login validation error”
- You add a new feature → make a commit: “Add user dashboard page”
- You update UI styling → make a commit: “Improve navbar design”
Good commits make it easier to understand project progress and roll back changes if needed.
Q11. What is git status used for?
git status is used to check the current state of your working directory and staging area.
It shows which files have been modified, which files are staged for commit, and which files are untracked.
This helps you understand exactly what changes are ready to be committed and what is still pending.
Key Points:
- Shows modified files that are not yet staged
- Shows files added to the staging area
- Displays untracked (new) files
- Helps prevent accidental commits
- Used frequently before running git commit
Q12. What is git add used for?
The git status command is used to check the current condition of your repository. It shows what is happening in your working directory and staging area before you make a commit.
When you run git status, Git tells you:
- Which files have been modified but not staged
- Which files are staged and ready to be committed
- Which files are untracked (new files Git is not tracking yet)
- Which branch you are currently working on
This command is very important because it helps you review your changes before committing. It reduces the chances of accidentally committing the wrong files or forgetting to add important changes.
In real development, programmers use git status frequently — usually before every commit — to stay aware of the project’s current state. That’s why it is considered one of the most commonly used Git commands.
Q13. What is git commit -m used for?
The command git commit -m is used to create a new commit along with a message written directly in the terminal.
The -m flag stands for message, and it allows you to describe the changes you are saving in that commit.
When you run this command, Git takes all the staged changes and saves them as a snapshot in the repository history. The message you provide explains what was changed and why.
Key Points:
- Creates a commit from staged files
- Adds a commit message in the same command
- Saves changes permanently in project history
- Helps track what was modified in each update
Clear and meaningful commit messages are important because they make the project history easy to understand. In team projects, good commit messages improve collaboration and make debugging much easier.
Q14. What is a branch in Git?
A branch is an independent line of development. It allows working on features without affecting main code.
Branches are cheap and fast. Most workflows use feature branches.
Branching improves stability and productivity.
Q15. What is merge conflict?
A merge conflict occurs when Git cannot automatically merge changes. It happens when the same file lines are modified.
Developers must manually resolve conflicts. Conflict resolution is a common interview topic. Proper branching reduces conflicts.
Q16. What is .gitignore file?
.gitignore tells Git which files to ignore. It prevents committing logs, secrets, or build files. It improves repository cleanliness.
Each project should include a .gitignore file. It enhances security and performance.
Q17. What is a remote repository?
A remote repository is a version of the project hosted online. GitHub is the most common remote platform. Remotes allow team collaboration. Developers push and pull changes from remotes. It keeps everyone in sync.
Q18. What is git push used for?
git push uploads local commits to a remote repository. It shares changes with the team.
Pushing updates GitHub branches. Without push, changes stay local. Push is required for collaboration.
Q19. What is a pull request in GitHub?
A pull request requests merging changes into another branch. It enables code review and discussion.
Teams review code before merging. Pull requests improve code quality. They are central to GitHub workflows.
Q20. Why is GitHub important for developers?
GitHub enables collaboration, version control, and code hosting. It supports CI/CD, issue tracking, and reviews.
Recruiters often check GitHub profiles. It showcases developer skills. GitHub is essential in modern software development.