Q1. What is JavaScript and how does it run in the browser?
- JavaScript is a programming language used to make web
pages interactive. Without it, websites can only display static content
like text and images. - When a website is opened in a browser, JavaScript runs inside a built-in
JavaScript engine. For example, Google Chrome uses the
V8 engine. - The engine reads the JavaScript code, converts it into instructions the
computer understands, and then executes those instructions. - This entire process happens very quickly, which is why buttons, menus,
and animations respond instantly on modern websites. - JavaScript can modify HTML and CSS while
the page is already open using the Document Object Model (DOM). - Because of this ability, JavaScript is essential for building
dynamic web applications such as forms, pop-ups,
sliders, live search, and dashboards.
Q2. What is the DOM and how does JavaScript interact with it?
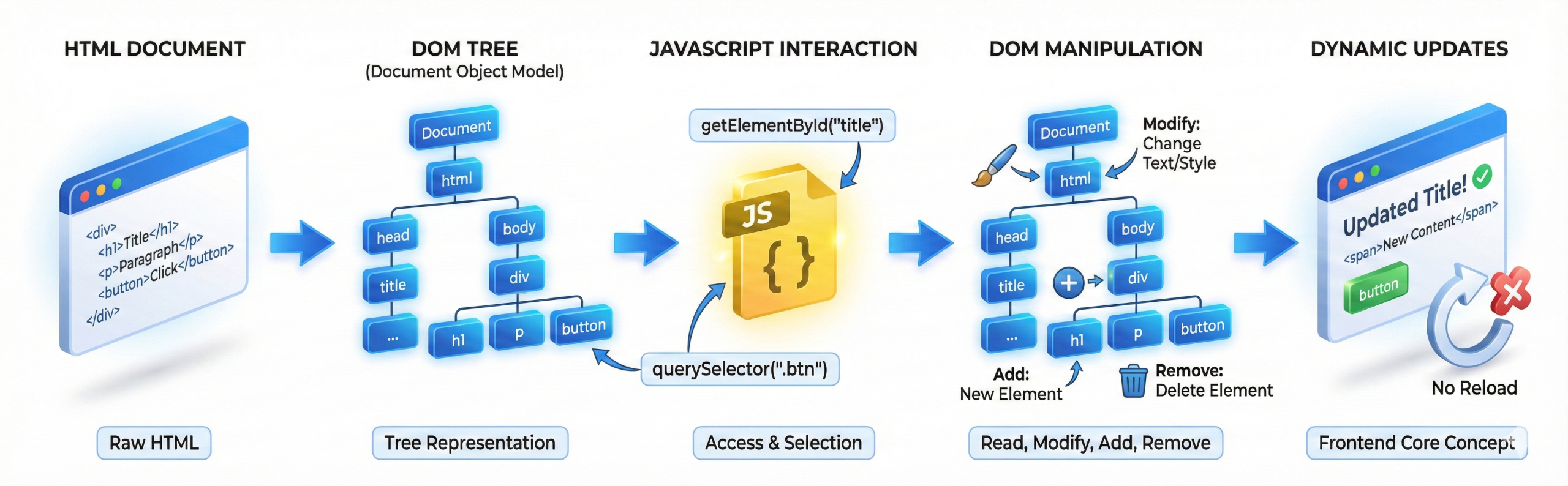
- The DOM (Document Object Model) is a tree-like structure that represents an HTML document inside the browser.
- Each HTML element becomes a node in this tree, which allows JavaScript to access and control it.
- JavaScript interacts with the DOM using methods like getElementById(), querySelector(), and querySelectorAll() to read or modify content.
- Using DOM manipulation, we can add, remove, or update elements without reloading the page.
- This is why features like form validation, dynamic content updates, pop-ups, and live search work smoothly.
- Understanding DOM manipulation is very important in frontend interviews because it shows how well you understand how browsers and JavaScript work together.
Q3. How does event handling work in JavaScript?
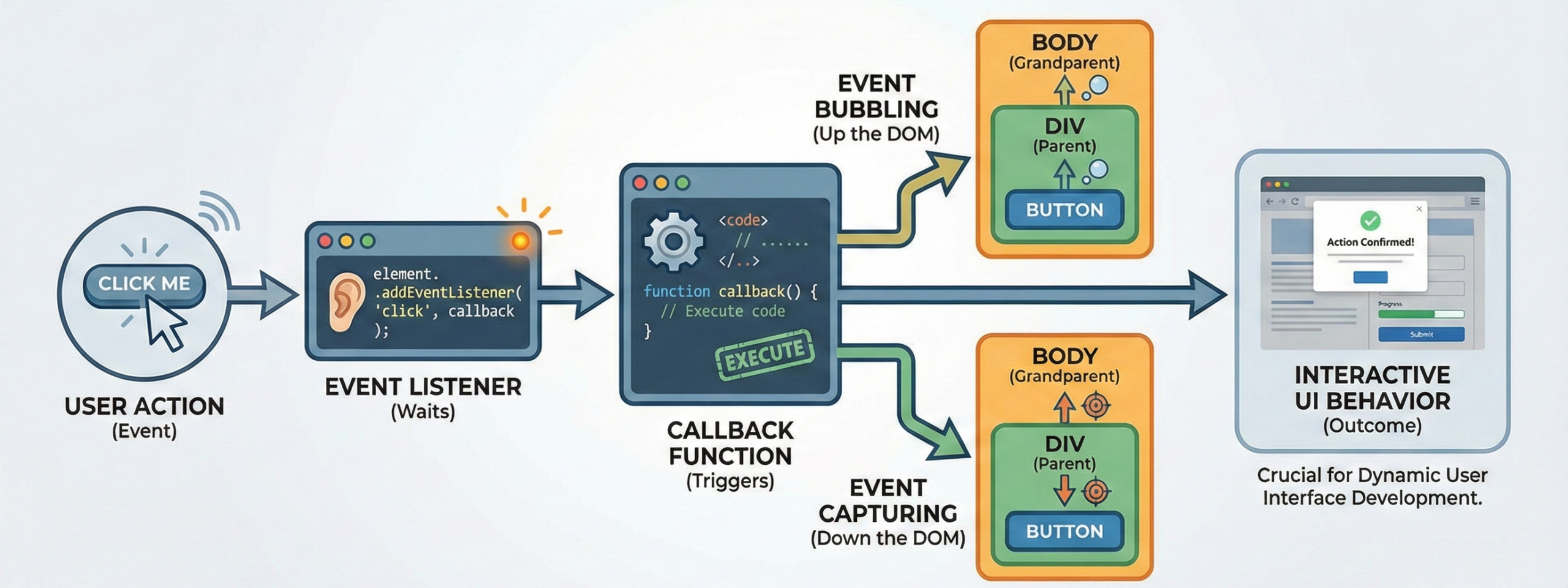
JavaScript Event Handling allows a webpage to respond to user actions such as clicks, key presses, scrolling, or form submissions. These actions are called events.
An event listener is used to detect when a specific event happens. When the event occurs, it runs a function called a callback function. This is how buttons perform actions, forms validate input, and menus open or close.
Events in JavaScript follow two main phases: bubbling and capturing. In bubbling, the event starts from the target element and moves upward through parent elements. In capturing, it moves from the top of the DOM tree down to the target element.
This event system makes websites interactive and dynamic. A strong understanding of events is essential for building modern user interfaces and is a common topic in frontend interviews.
Q4. How does Tkinter handle user events like button clicks?
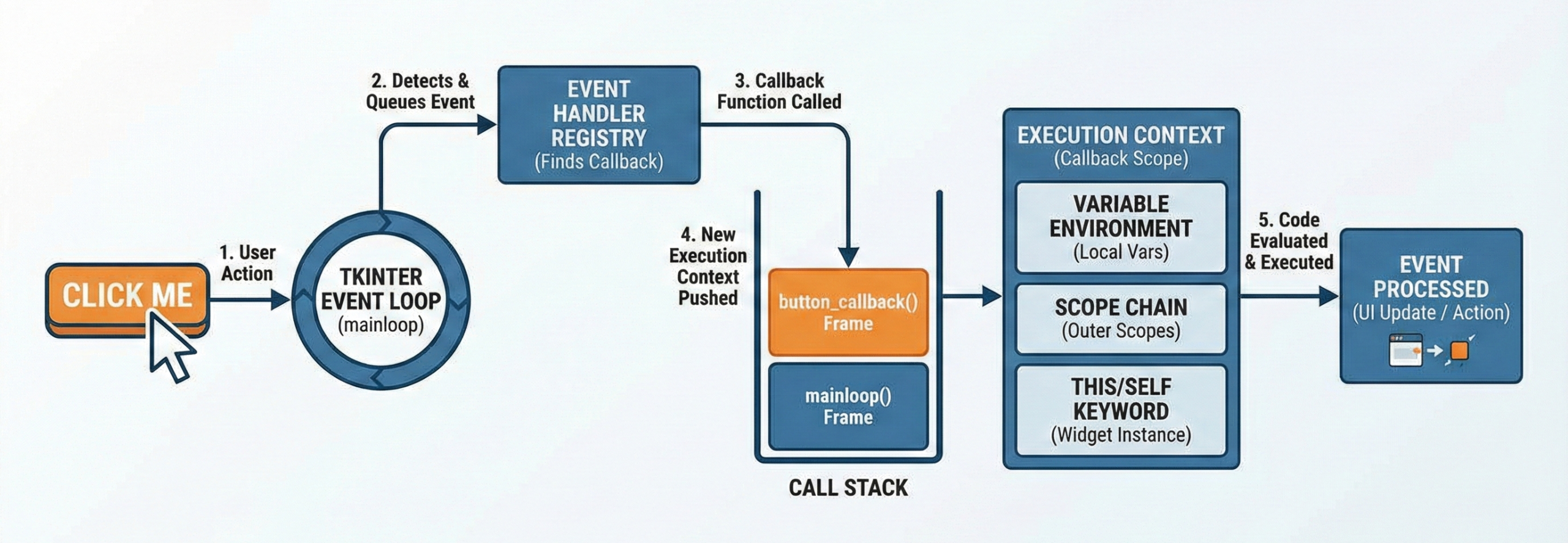
The execution context defines how JavaScript code is evaluated and executed.
It contains important parts like the variable environment,
the scope chain, and the value of the this keyword.
JavaScript uses a call stack to manage execution contexts.
Every time a function is called, a new execution context is created and pushed onto the stack.
When the function finishes, it is removed from the stack.
This internal process helps us understand how functions run, how variables are accessed,
and how scope works in real JavaScript applications.
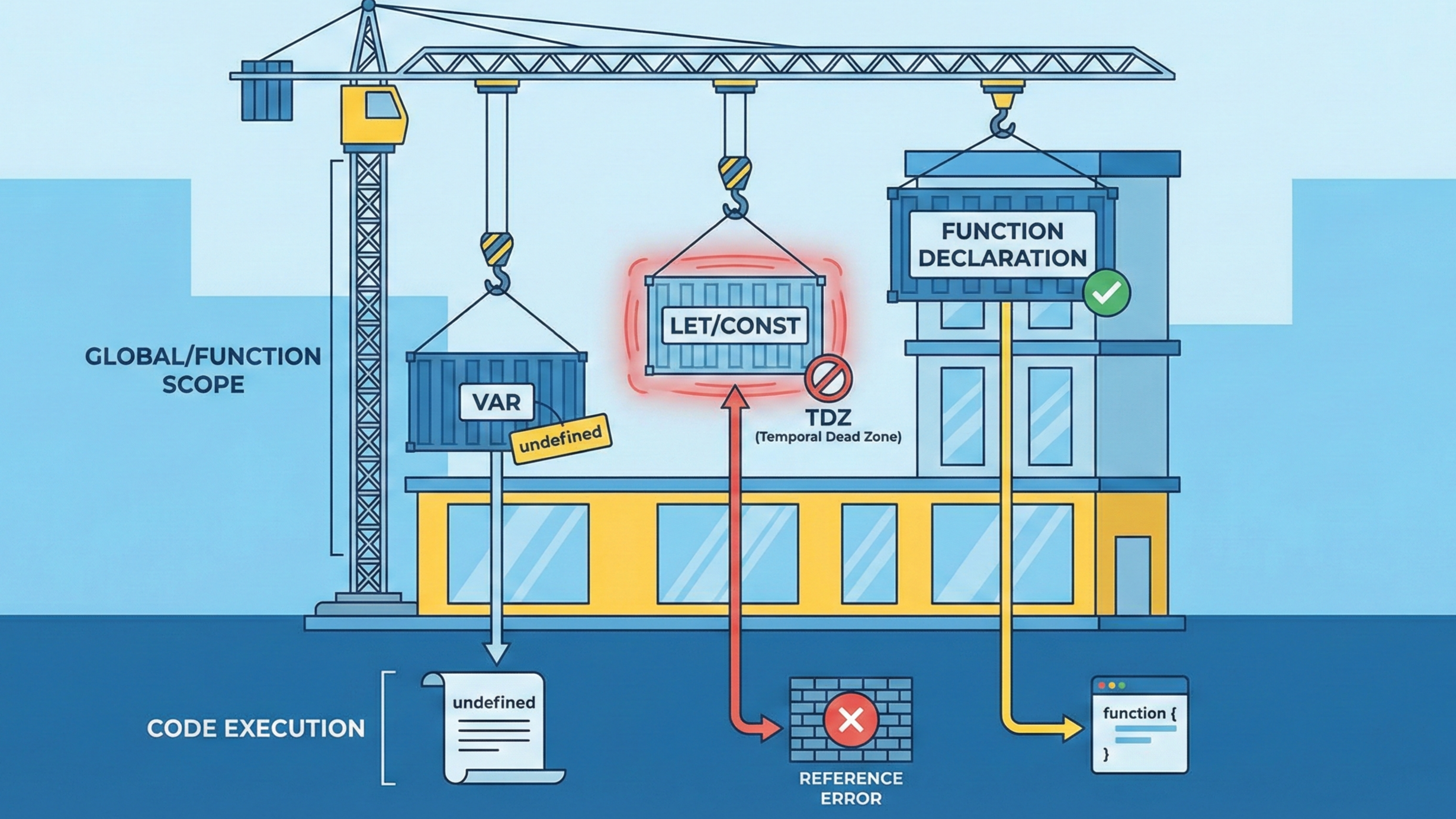
Q5. Difference between var, let, and const.
| Feature | var | let | const |
| Scope | Function | Block | Block |
| Re-declare | Yes | No | No |
| Re-assign | Yes | Yes | No |
| Hoisting | Yes | Yes (TDZ) | Yes (TDZ) |
Q6. Difference between == and ===.
| Operator | Comparison | Type Check | Use |
| == | Value | No | Avoid |
| === | Value + Type | Yes | Preferred |
| Result | Implicit conversion | Strict | Safer |
| Interview | Common trap | Best practice | ✔ |
Q7. Difference between function declaration and function expression
| Aspect | Declaration | Expression |
| Hoisting | Yes | No |
| Syntax | function f() | const f = () => |
| Use | Global/local | Assigned to variable |
| Modern Use | Less | More |
Q8. Difference between null and undefined.
| Feature | null | undefined |
| Meaning | Intentional empty | Not assigned |
| Type | object | undefined |
| Set by | Developer | JavaScript |
| Interview | Common | Very common |
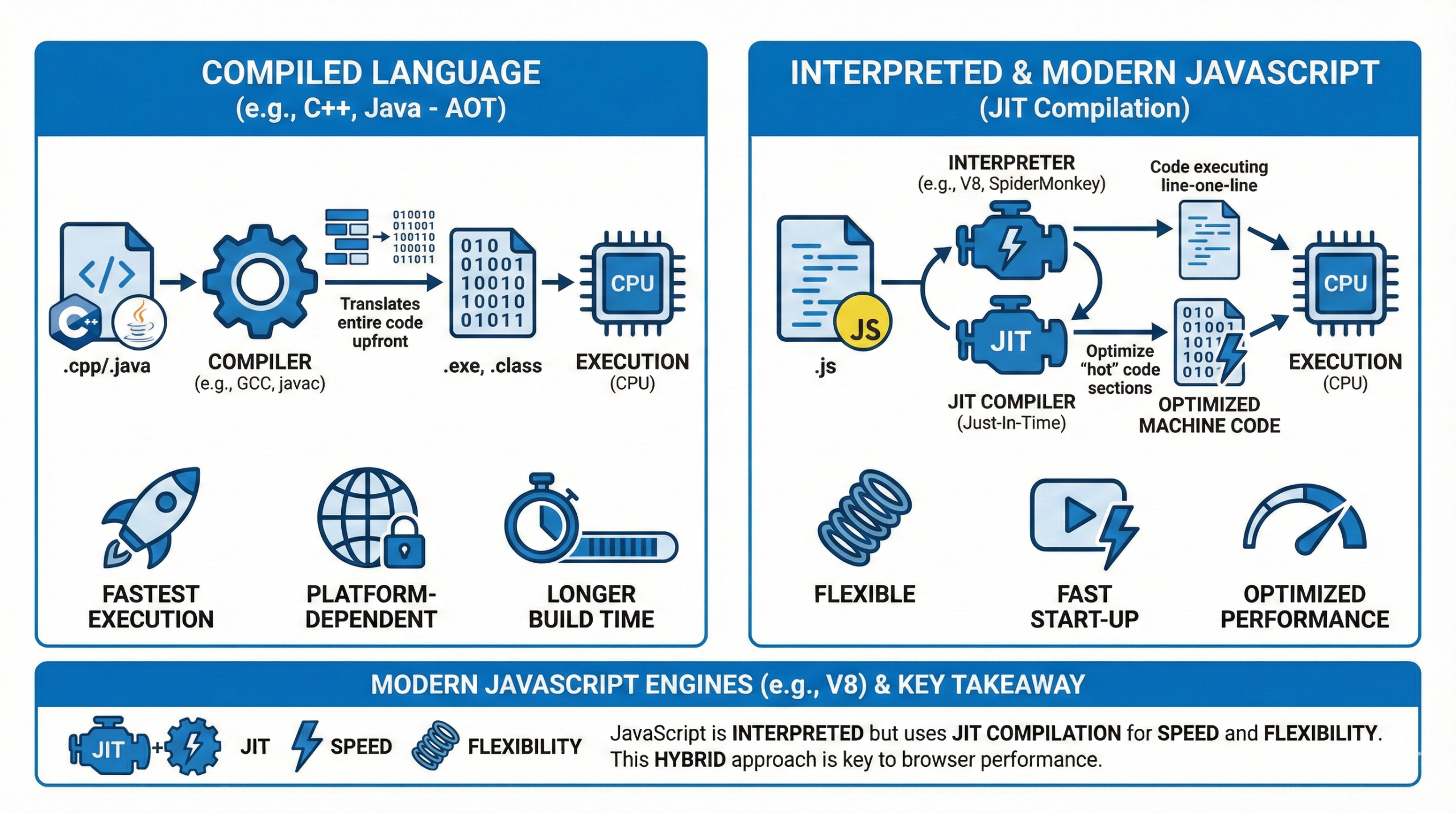
Q9. Is JavaScript a compiled or interpreted language?
JavaScript is interpreted but modern engines use JIT (Just-In-Time) compilation. Code is executed line by line with optimizations.
This makes JavaScript fast and flexible. Interviewers often expect this explanation.
It explains browser performance.
Q10. What are data types in JavaScript?
JavaScript has primitive types like string, number, boolean, null, undefined, symbol, and bigint. Objects are non-primitive.
Dynamic typing allows variables to change types.
Understanding data types avoids runtime errors. This is a basic interview topic.
Q11. What is hoisting in JavaScript?
Hoisting moves variable and function declarations to the top of their scope.
var is hoisted but initialized as undefined. let and const are hoisted but not accessible before declaration.
This explains unexpected undefined values. Hoisting questions are very common.
Q12. What is scope in JavaScript?
Scope defines where variables can be accessed.
JavaScript has global, function, and block scope. let and const respect block scope.
Proper scoping prevents bugs. This is essential for clean code.
Q13. What are JavaScript functions?
Functions are reusable blocks of code. They can take parameters and return values.
JavaScript supports normal, arrow, and anonymous functions.
Functions are first-class citizens. This means they can be passed as arguments.
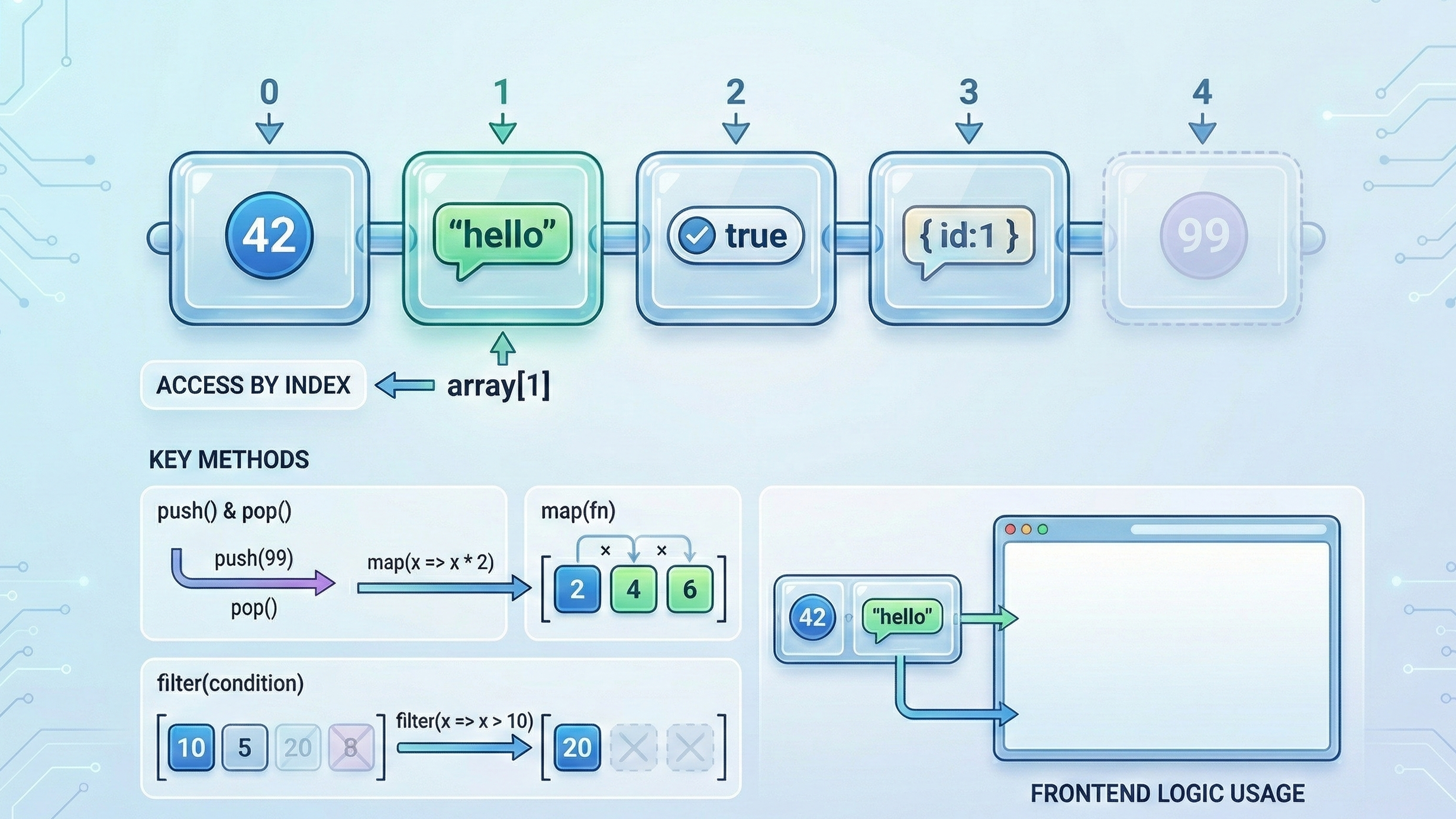
Q14. What is an array in JavaScript?
An array stores ordered collections of data. Elements are accessed by index.
Arrays support methods like push, pop, map, and filter.
Arrays are heavily used in frontend logic. Interviewers frequently ask this.
Q15. What is an object in JavaScript?
Objects store key-value pairs. They represent real-world entities.
Properties and methods define object behavior.
Objects are fundamental in JavaScript. Almost everything in JS is an object.
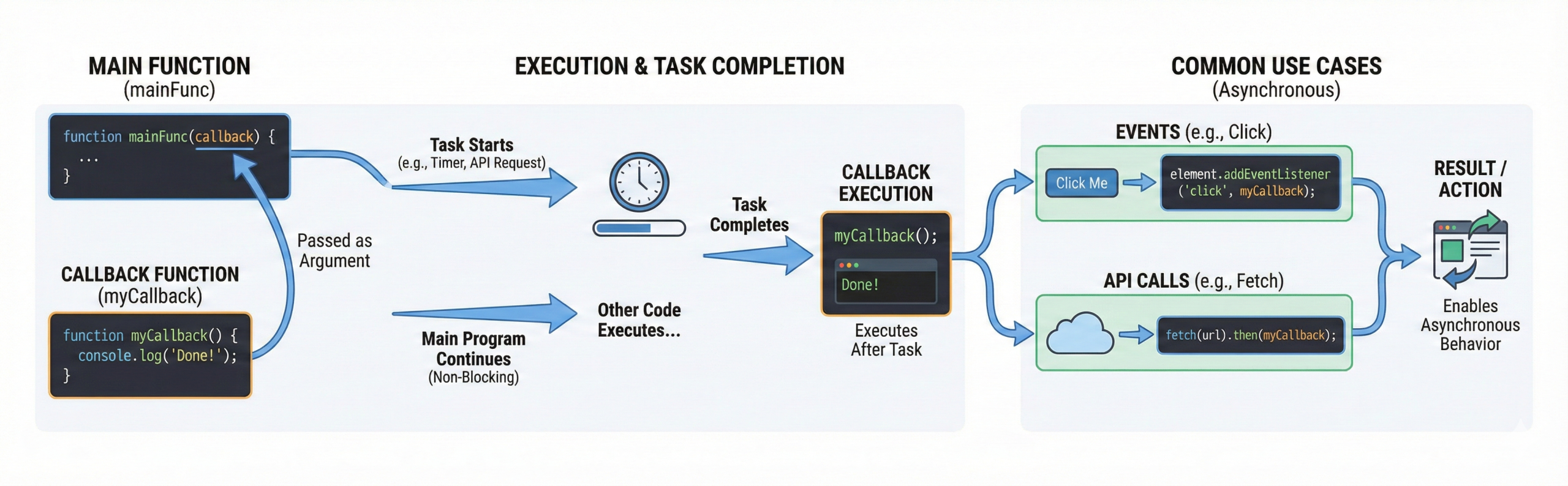
Q16. What is a callback function?
A callback is a function passed as an argument to another function. It executes after a task completes.
Callbacks enable asynchronous programming. They are used in events and API calls.
This is a core JS concept.
Q17. What is asynchronous JavaScript?
Asynchronous JS allows non-blocking execution. It uses callbacks, promises, and async/await.
This keeps applications responsive. API calls and timers use async behavior.
Interviews often test async understanding.
Q18. What is a promise?
A promise represents a future value. It can be pending, resolved, or rejected.
Promises handle async operations cleanly. They avoid callback hell.
Promises are widely used in APIs.
Q19. What is console.log() used for?
console.log() prints values to the browser console. It is used for debugging.
Developers inspect variables and logic flow.
It does not affect UI.
This is a simple but common interview question.
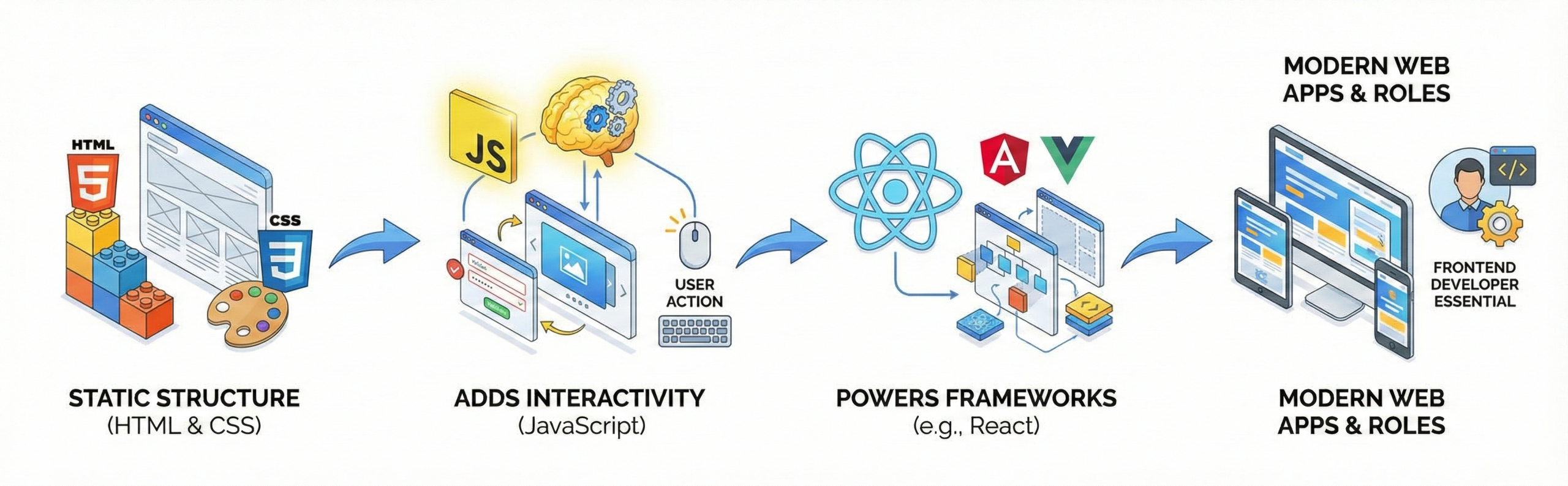
Q20. Why is JavaScript important for frontend development?
JavaScript adds interactivity to websites. It works with HTML and CSS.
Frameworks like React depend on JavaScript.
Modern web apps rely heavily on JS.
It is essential for frontend roles.