Q1. What is JSON and why is it widely used in applications?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format used to exchange data between different systems and applications.
It is easy for humans to read and write and simple for machines to parse and generate. JSON is language-independent, which makes it widely used in APIs and web services.
Most web and mobile applications use JSON for client-server communication. Its simple and compact structure makes it one of the most common formats used in real-world projects and interviews.
Q2. How is JSON data structured?
JSON data is structured using key-value pairs. Keys are always strings, and values can be strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, objects, or null.
Objects are enclosed in { } and arrays in [ ]. This format allows nesting of data to handle complex structures and relationships.
A proper JSON structure ensures smooth parsing, validation, and data exchange between systems.
Q3. How does JSON flow between client and server in an API?
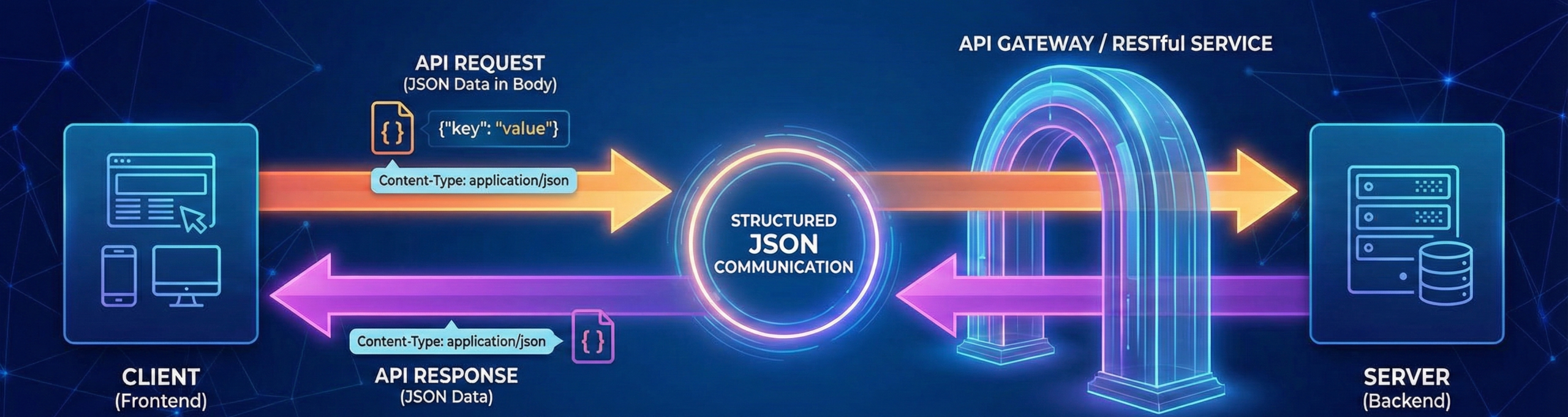
In APIs, the client sends a request containing JSON data in the request body. The server processes the request and responds with JSON.
Headers specify Content-Type: application/json, which tells the server how to read the incoming data.
JSON enables structured communication between frontend and backend systems. This request-response flow forms the backbone of RESTful services.
Q4. How is JSON converted to Python objects and vice versa?
Python converts JSON strings into dictionaries using json.loads().
Dictionaries are converted back into JSON strings using json.dumps().
This conversion makes it easy to manipulate data in Python programs.
JSON files can also be read and written using json.load() and json.dump(). This process is commonly asked in Python interviews.
Q5. Difference between JSON and XML
| Feature | JSON | XML |
| Format | Key-value | Tag-based |
| Readability | Easy | Verbose |
| Size | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Usage | APIs | Legacy systems |
Q6. Difference between JSON object and JSON array
| Feature | JSON Object | JSON Array |
| Structure | Key-value pairs | Ordered values |
| Brackets | { } | [ ] |
| Access | By key | By index |
| Use Case | Named data | Lists of data |
Q7. Difference between json.load() and json.loads() in Python
| Function | Input | Use Case |
| json.load() | File object | Read JSON file |
| json.loads() | String | Parse JSON string |
| Output | Python dict | Python dict |
| Usage | File handling | API responses |
Q8. Difference between json.dump() and json.dumps().
| Function | Output | Use Case |
| json.dump() | File | Write JSON to file |
| json.dumps() | String | Convert to JSON string |
| Storage | Persistent | Temporary |
| Usage | Save data | Send data |
Q9. Is JSON a programming language?
Python converts JSON strings into dictionaries using json.loads().
Dictionaries are converted back into JSON strings using json.dumps().
This conversion makes it easy to manipulate data in Python programs.
JSON files can also be read and written using json.load() and json.dump(). This process is commonly asked in Python interviews.
Q10. What data types does JSON support?
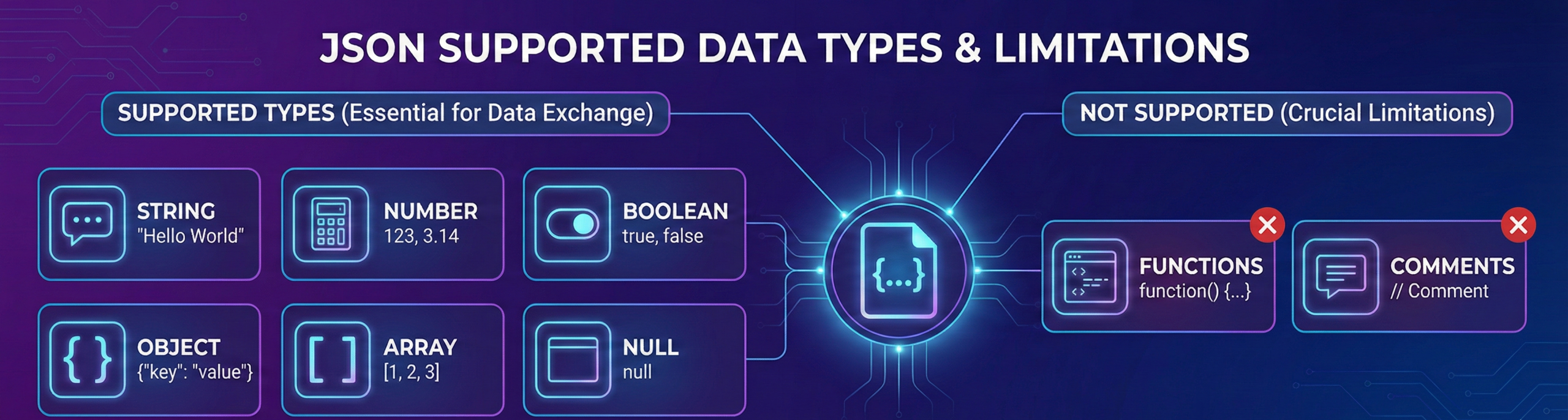
JSON supports string, number, boolean, object, array, and null data types.
It does not support functions or comments.
These basic data types cover most data-exchange needs in web applications.
Understanding JSON data types is essential for API development and is often asked in interviews.
Q11. What is a JSON key?
A JSON key is the name used to identify a value inside a JSON object.
It works like a label that tells us what the stored data represents. Every key connects directly to one value.
Key Points:
- A JSON key is always written as a string.
- Keys must be enclosed in double quotes (” “).
- Each key maps to exactly one value.
- Keys should be unique within the same object.
- Clear and meaningful key names improve readability.
Q12. Can JSON store nested data?
Yes, JSON supports nested objects and arrays.
Nested structures allow us to represent complex relationships inside data.
APIs often return deeply nested JSON structures.
Python can easily parse nested JSON into dictionaries.
Handling nested JSON is a practical and important skill.
Q13. What is a JSON file extension?
JSON files use the .json extension. These files store structured data in text format.
They are commonly used for configuration files. JSON files are platform-independent. They are easy to read and edit.
Q14. What is serialization in JSON?
Serialization is the process of converting a Python object (like a dictionary or list) into JSON format.
It is required when sending data over a network or storing it in a file.
Python provides json.dumps() and json.dump() for this purpose.
Key Points:
- json.dumps() converts a Python object into a JSON string.
- json.dump() writes JSON data directly into a file.
- Serialization makes data transferable between systems.
- It is commonly used in APIs and web applications.
Q15. What is deserialization in JSON?
Deserialization is the process of converting JSON data back into Python objects.
It allows your program to read and use data received from APIs or files.
It is the reverse process of serialization.
Key Points:
- json.loads() converts a JSON string into a Python object.
- json.load() reads JSON data from a file and converts it into Python objects.
- It is commonly used when working with API responses.
- Deserialization makes JSON data usable inside Python programs.
import json
# Example 1: Using json.loads() with JSON string
json_string = '{"name": "Anil", "age": 22, "city": "Jaipur"}'
python_data = json.loads(json_string)
print(python_data)
print(type(python_data)) # <class 'dict'>
# Example 2: Using json.load() with JSON file
with open("data.json", "r") as file:
file_data = json.load(file)
print(file_data)
print(type(file_data)) # <class 'dict'>
Q16. Can JSON handle comments?
No, JSON does not support comments. Adding comments will cause parsing errors.
This keeps JSON simple and strict in structure.
Some developers confuse JSON with JavaScript objects.
Interviewers often check this detail.
Q17. What is Content-Type application/json?
Content-Type: application/json is an HTTP header that tells the server that the data being sent in the request body is in JSON format.
It helps the server correctly understand and process the incoming data.
Without this header, the server may not recognize the data format and can reject the request.
Key Points:
- It informs the server about the format of the request body.
- Commonly used in REST APIs when sending JSON data.
- Required in POST, PUT, or PATCH requests that send JSON.
- Ensures proper communication between client and server.
import requests
url = "https://api.example.com/data"
data = {
"name": "Anil",
"age": 22
}
response = requests.post(
url,
json=data,
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"}
)
print(response.status_code)
Q18. How do you validate JSON data?
JSON validation ensures that the data follows the correct structure and data types.
It helps prevent runtime errors and improves API reliability.
In Python, we can validate JSON using the jsonschema library.
import json
from jsonschema import validate, ValidationError
# Sample JSON data
data = {
"name": "Anil",
"age": 22,
"city": "Jaipur"
}
# Define JSON Schema
schema = {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"age": {"type": "number"},
"city": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["name", "age", "city"]
}
try:
validate(instance=data, schema=schema)
print("JSON is valid")
except ValidationError as e:
print("JSON is invalid")
print("Error:", e.message)
Q19. Why is JSON preferred over CSV for APIs?
JSON supports structured and nested data, while CSV is limited to flat, tabular data.
Because of this, JSON is more suitable for APIs and modern web applications that require organized and hierarchical responses.
| Feature | JSON | CSV |
| Data Structure | Nested (objects & arrays) | Flat (rows & columns) |
| Complex Data Support | Yes | Limited |
| API Usage | Widely used | Rarely used |
| Readability | Structured and descriptive | Simple but limited |
| Best For | Web apps, APIs, structured data | Simple tabular data |
Q20. Why is JSON important for backend developers?
JSON is the standard data format for APIs. Backend systems constantly send and receive JSON.
Python frameworks like Flask and Django use JSON heavily. Understanding JSON is mandatory for interviews. It connects frontend, backend, and databases.